Professor Jiwon Jang and Seungbok Yang, a PhD candidate, from the Department of Life Sciences at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), and Dr. Mahdi Golkaram from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at University of California Santa Barbara (UCSB) have uncovered a novel regulator governing how cells respond to mechanical cues. Their findings were published on May 3 in the online edition of Nature Cell Biology, an international journal in the field of cell biology.

Credit: POSTECH
Professor Jiwon Jang and Seungbok Yang, a PhD candidate, from the Department of Life Sciences at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), and Dr. Mahdi Golkaram from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at University of California Santa Barbara (UCSB) have uncovered a novel regulator governing how cells respond to mechanical cues. Their findings were published on May 3 in the online edition of Nature Cell Biology, an international journal in the field of cell biology.
Much research in cell biology has traditionally centered on understanding how cells react to chemical signals such as diffusible signaling molecules. However, cells also respond to mechanical stimuli such as cell density, size, and substrate stiffness by expressing specific genes. Yet, the mechanisms by which mechanical regulators perceive mechanical stimuli have remained largely unexplored.
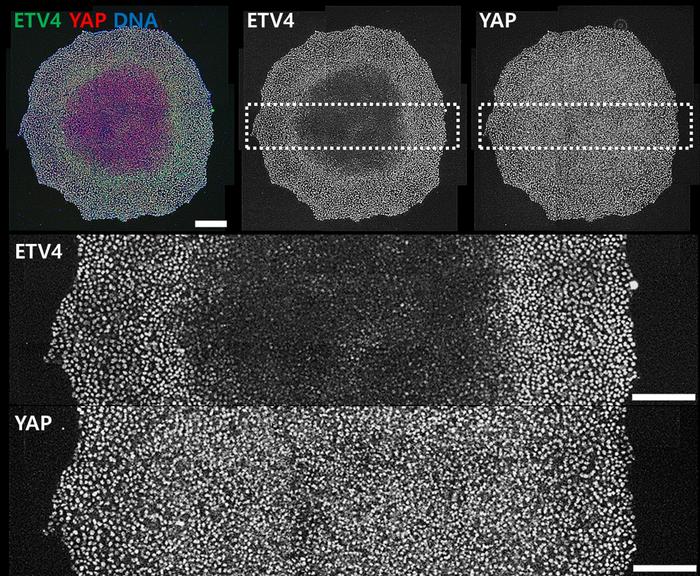
In this research, human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) were employed by the researchers to delve into how cells detect and react to mechanical signals. Through an examination of the transcriptome of hESCs cultivated under different cell densities, the researchers pinpointed a key player known as “ETV4”, responsible for mediating variations in stem cell density and controlling differentiation.
Furthermore, the team deciphered the intricate mechanism through which ETV4 perceives mechanical cues. Initially, integrin receptors1) recognize alterations in cell density, subsequently modulating the endocytosis of a cell surface receptor, namely the Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor (FGFR). Mechanical regulation of FGFR endocytosis determines the protein stability of ETV4 by ERK signaling.
During the differentiation process of stem cells, ETV4 plays a role in directing the formation of mesendoderm in regions characterized by low cell density while promoting neuroectoderm development in areas of high cell density. The researchers discovered that a new mechanotransducer ETV4 bridges cell density dynamics to stem cell differentiation.
POSTECH Professor Jiwon Jang who led the research stated, “We’ve uncovered the importance of mechanical cues in regulating stem cell differentiation along with the pivotal involvement of ETV4.” He expressed optimism by saying, “Given ETV4’s substantial implications as a critical oncogene, we envision leveraging this insight to devise technologies aimed at controlling cancer cells through mechanical cues.”
The research was conducted with support from the Biomedical Technology Development Program, the Basic Research Program for Individuals, the Group Research and Basic Research Lab Program, and the Smart Specialization Infrastructure Project of the National Research Foundation of Korea.The research was conducted with support from the Biomedical Technology Development Program, the Basic Research Program for Individuals, the Group Research and Basic Research Lab Program, and the Smart Specialization Infrastructure Project of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Journal
Nature Cell Biology
Article Title
ETV4 is a mechanical transducer linking cell crowding dynamics to lineage specification
Article Publication Date
3-May-2024