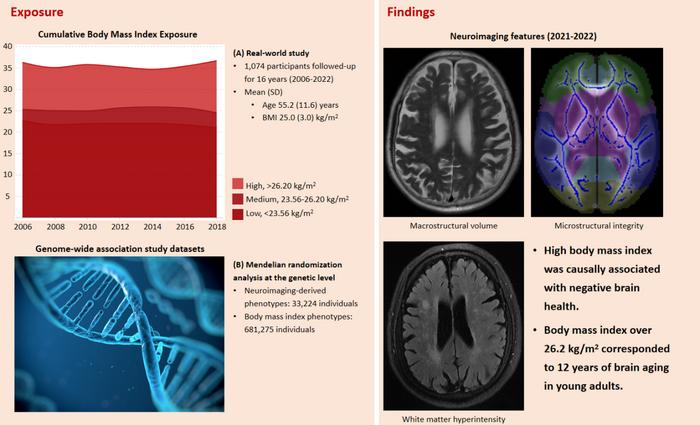
A recent study published in Health Data Science, a Science Partner Journal, reveals the significant impact of high cumulative body mass index (BMI) on brain health. The research, led by Associate Professor Han Lv from Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, found that high BMI is associated with smaller brain volume, larger white matter lesions, and abnormal microstructural integrity.

Credit: Lv, Han; Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University
A recent study published in Health Data Science, a Science Partner Journal, reveals the significant impact of high cumulative body mass index (BMI) on brain health. The research, led by Associate Professor Han Lv from Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, found that high BMI is associated with smaller brain volume, larger white matter lesions, and abnormal microstructural integrity.
The study analyzed data from a 16-year population-based cohort to investigate the effects of cumulative BMI on neuroimaging features in adults aged 25 to 83 years. Researchers discovered that high BMI was linked to smaller brain volume and larger volumes of white matter hyperintensity (WMH), particularly in adults younger than 45 years and those older than 60 years.
“High cumulative BMI is detrimental to brain health, especially for younger adults under 45 years, where it corresponds to approximately 12 years of brain aging,” said Associate Professor Han Lv. “Maintaining a BMI below 26.2 kg/m² is suggested for better brain health.”
The study utilized a generalized linear model to evaluate the association between cumulative BMI and various neuroimaging features, including brain macrostructure, white matter integrity, and brain microstructure. Additionally, Mendelian randomization analysis was performed to establish causal relationships using genetic data.
The results indicated that high BMI is causally linked to smaller gray matter volume and increased fractional anisotropy in certain brain regions, highlighting the importance of maintaining a healthy BMI throughout adulthood to preserve brain health.
“This research provides crucial insights into the relationship between BMI and brain health, emphasizing the need for public health strategies to control BMI for better neurological outcomes,” concluded Associate Professor Han Lv. “Future studies should focus on acquiring longitudinal neuroimaging data to further explore these associations.”
Journal
Health Data Science
Article Title
Association between Body Mass Index and Brain Health in Adults: A 16-Year Population-Based Cohort and Mendelian Randomization Study
Article Publication Date
15-Mar-2024