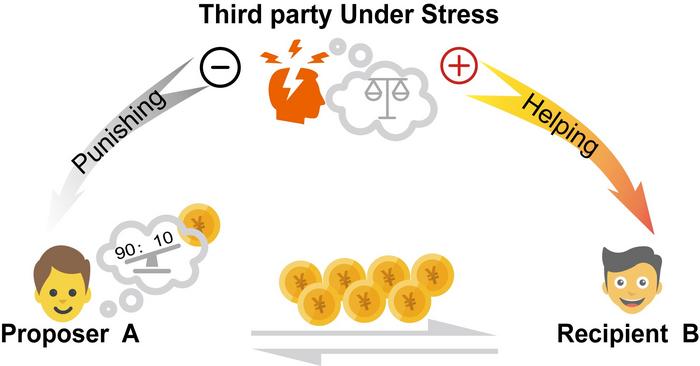
Being stressed while witnessing injustice may push your brain towards altruism, according to a study published on May 14th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Huagen Wang from Beijing Normal University, China, and colleagues.

Credit: Huagen Wang (CC-BY 4.0,
Being stressed while witnessing injustice may push your brain towards altruism, according to a study published on May 14th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Huagen Wang from Beijing Normal University, China, and colleagues.
It takes more cognitive effort to punish others than it does to help them. Studies show that when witnessing an act of injustice while stressed, people tend to behave selflessly, preferring to help the victim than to punish the offender. This aligns with theories proposing that distinct brain networks drive intuitive, fast decisions and deliberate, slow decisions, but precisely how a bystander’s brain makes the trade-off between helping and punishing others in stressful situations is unclear.
To better understand the neural processes driving third-party intervention in the face of injustice, Wang and colleagues recruited 52 participants to complete a simulated third-party intervention task in an fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) scanner, where they watched someone decide how to distribute an endowment of cash between themself and another character, who had to passively accept the proposal. The participant then decided whether to take money away from the first character, or give money to the second. Roughly half of these participants submerged their hands in ice water for three minutes right before starting the task to induce stress.
Acute stress affected decision-making in extremely unfair situations, where the participant witnessed someone keep the vast majority of the cash they were supposed to split with someone else. The researchers observed higher dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) activation—a brain region typically linked to mentalizing and decision-making—when stressed participants chose to punish an offender. Computational modeling revealed that acute stress reduces bias towards punishment, raising the likelihood that someone will help a victim instead.
The authors state that their findings suggest that punishing others requires more deliberation, cognitive control, and reliance on calculations than helping a victim. These results align with a growing body of evidence suggesting that stressed individuals tend to act more cooperatively and generously, perhaps because people devote more of their cognitive resources towards deciding how to help the victim, rather than punishing the offender.
The authors add, “Acute stress shifts third-party intervention from punishing the perpetrator to helping the victim.”
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology:
Citation: Wang H, Wu X, Xu J, Zhu R, Zhang S, Xu Z, et al. (2024) Acute stress during witnessing injustice shifts third-party interventions from punishing the perpetrator to helping the victim. PLoS Biol 22(4): e3002195.
Author Countries: China
Funding: The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (https://www.nsfc.gov.cn/english/site_1/index.html, 32271092 to CL and 32130045 to SQ), Major Project of National Social Science Foundation ( , 19ZDA363 to CL) and Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission ( , Z151100003915122 to CL). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Journal
PLoS Biology
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
People
COI Statement
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.