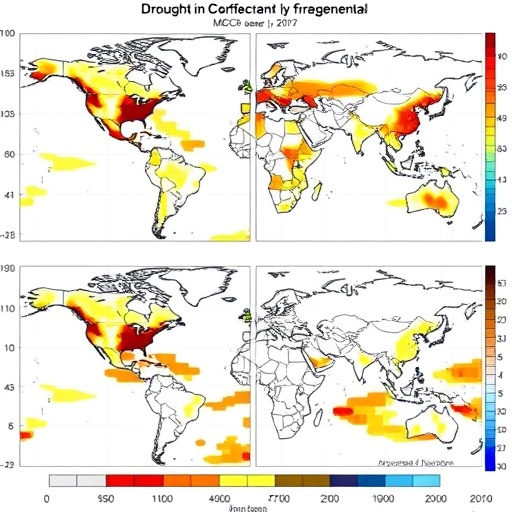
Drought is one of the most significant environmental challenges facing many regions across the globe today. It affects agricultural productivity, water resources, and the overall ecological balance. In recent years, the necessity for an effective assessment and prediction mechanism has become increasingly urgent as climate change exacerbates the severity and frequency of drought events. A breakthrough comes from a recent study led by Yousaf et al., who have introduced a novel Bi-weight Mid Correlation Coefficient Divergence (BMCCD) approach designed for multi-model ensemble-based drought assessment. This innovative methodology provides an efficient and robust framework for better understanding and anticipating drought conditions.
Current methodologies in drought assessment often suffer from limitations in their ability to capture the complex dynamics of hydrological and meteorological variables. Traditional drought indices, while useful, can often exhibit a lack of precision, especially when applied to multi-model ensembles. This is where the BMCCD approach distinguishes itself, offering a solution that emphasizes weighing correlations adequately to enhance the reliability of drought predictions. By integrating multiple models, BMCCD empowers researchers and policymakers with the content they need to make informed decisions regarding water management and agriculture.
The Bi-weight Mid Correlation Coefficient Divergence technique revolves around the idea of assigning weights to different correlation coefficients derived from varied models. This ensures that the influence of outlier data points is minimized while still acknowledging their potential significance. The approach relies on the robust statistical properties of bi-weight functions, enhancing the final assessment’s accuracy and reliability. By maintaining focus on numerous models, BMCCD integrates findings from diverse climatic and geographical scenarios, promoting a comprehensive understanding of drought impacts.
In testing their methodology, Yousaf et al. applied BMCCD to a range of datasets representing different climate zones. The initial results were promising, showcasing a marked improvement in the correlation of model outputs with observed drought conditions. This enhancement in predictive capability allows for more timely interventions that could mitigate the adverse effects of drought on agriculture and water supply. Furthermore, the study demonstrated that utilizing ensemble models provides a broader predictive landscape, enabling better strategies for resource allocation and usage.
The implications of the BMCCD framework extend beyond mere prediction; they usher in a potential paradigm shift in how drought assessments are conducted globally. Policymakers may find this framework to be indispensable when crafting responses to extreme weather events similar to droughts. By relying on a multifaceted approach that considers various model outputs, decision-makers can build more resilient agricultural and water management policies. Moreover, the application of this technique fosters collaborative efforts among scientists, water resource managers, and agricultural stakeholders, ensuring all parties are adequately informed.
The research also highlights the importance of data quality and the selection of appropriate models in constructing effective ensemble systems. The study emphasizes that while the BMCCD approach significantly enhances predictive accuracy, the underlying data must be rigorously vetted. The inclusion of poor-quality data or models that do not adequately represent the study phenomena could lead to misleading results. Therefore, the careful selection of models combined with the robust application of BMCCD can yield substantial benefits.
In the context of climate change, the introduction of models like BMCCD becomes particularly critical. As precipitation patterns shift and temperatures rise, conventional models may falter in their efficacy. The BMCCD framework provides an opportunity for researchers and practitioners to refine their predictive capabilities amid these evolving conditions. The resultant synthesis of models allows for a flexibility that can adapt to unforeseen changes in climate, thereby sustaining agricultural productivity and ensuring water availability.
Moreover, as drought increasingly threatens food security worldwide, the BMCCD approach not only improves drought assessment but also ensures that subsequent agricultural practices align with realistic forecasts. By anticipating drought conditions with heightened precision, farmers can adapt their practices to better prepare for such eventualities. This could mean altering planting schedules, selecting drought-resistant crop varieties, or implementing advanced irrigation strategies.
However, transitioning to this new paradigm also involves an educational component. For the BMCCD framework to reach its full potential, stakeholders at all levels must understand its applications and benefits. This includes training workshops, academic publications, and collaborations across sectors. Ultimately, widespread understanding will facilitate better adoption and minimize resistance to integrating innovative methodologies into existing practices.
The research conducted by Yousaf and his collaborators is a significant step forward in drought assessment. The BMCCD technique extends beyond conventional methodologies, presenting a promising tool for the future. As it gains traction, it will be crucial to monitor its implementation in real-world scenarios and to continually refine the approach based on collected data and outcomes.
In summary, the sustained impact of the BMCCD framework for drought assessment epitomizes the power of scientific innovation in addressing pressing environmental challenges. As the world grapples with the ramifications of climate change, this approach offers renewed hope for effective drought management. The potential for improved predictive accuracy, coupled with a robust understanding of data inputs, lays the groundwork for a future where agricultural vulnerabilities are reduced, and water resources are utilized more sustainably.
The ongoing collaboration between researchers, policymakers, and affected communities will ultimately determine the effectiveness of the BMCCD approach. A joint commitment to advancing drought assessment methods will benefit all stakeholders involved, and it could serve as a model for similar initiatives across other environmental challenges. The quest for resilient ecosystems and sustainable practices hinges on our ability to adapt and innovate, and the introduction of BMCCD marks a significant contribution towards that endeavor.
In the coming years, as the BMCCD framework integrates more adeptly into the landscape of drought assessment, further studies and applications are anticipated. Researchers are already considering its adaptation to other contexts, such as assessing flood risks or other extreme weather phenomena. This adaptability is a testament to the crucial role that innovation will play in shaping resource management and environmental stewardship in a changing world.
Subject of Research: Drought assessment using a novel Bi-weight Mid Correlation Coefficient Divergence (BMCCD) approach.
Article Title: A novel Bi-weight Mid Correlation Coefficient Divergence (BMCCD) approach for multi-model ensemble-based drought assessment.
Article References: Yousaf, M., Shafique, L., Qamar, S. et al. A novel Bi-weight Mid Correlation Coefficient Divergence (BMCCD) approach for multi-model ensemble-based drought assessment. Environ Monit Assess 197, 1111 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-025-14578-2
Image Credits: AI Generated
DOI:
Keywords: Drought assessment, Bi-weight Mid Correlation Coefficient Divergence, multi-model ensemble, climate change, water management, agricultural productivity.