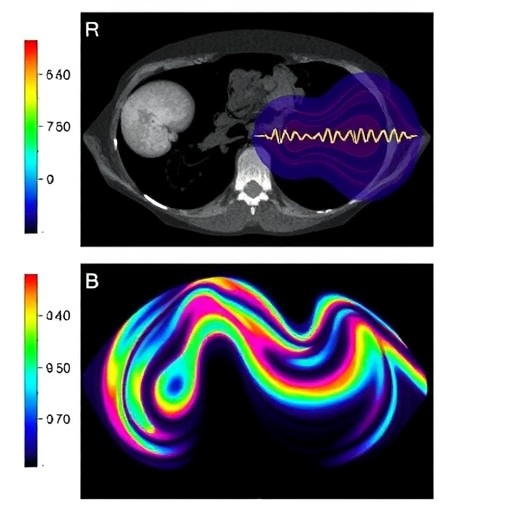
In a groundbreaking study, researchers have introduced a novel imaging technique that utilizes bidimensional shear wave elastography (bSWE) to examine splenic stiffness as a diagnostic tool for esophageal varices in children suffering from portal hypertension. This innovative approach holds the promise to transform how medical professionals evaluate and manage this serious condition, ultimately aiming to enhance patient care and outcomes. The study, led by Mackintosh et al., highlights the urgency of new diagnostic modalities as portal hypertension poses significant health risks for pediatric patients, necessitating reliable and non-invasive assessment methods.
Portal hypertension, characterized by increased pressure in the portal venous system, can lead to a variety of complications, including esophageal varices. These varices are distended veins in the esophagus that can rupture, leading to potentially fatal bleeding. Traditionally, the assessment of esophageal varices in children relies on invasive procedures such as endoscopy. However, the implementation of bidimensional shear wave elastography for liver and spleen assessment provides an intriguing alternative that favors non-invasive techniques and promises enhanced safety for young patients.
Shear wave elastography operates on the principles of ultrasound technology, where sound waves are utilized to evaluate tissue stiffness. By analyzing the speed of these waves as they travel through the spleen, clinicians gain insights into the stiffness of the organ, which correlates with the severity of portal hypertension. This technique leverages advancements in acoustic imaging, allowing for real-time assessments without the need for sedation or hospitalization, making it notably advantageous for pediatric patients who may experience heightened anxiety associated with invasive procedures.
During the study, the authors meticulously evaluated children diagnosed with portal hypertension, using bSWE to measure splenic stiffness. Their results indicated a significant correlation between increased spleen stiffness and the presence as well as severity of esophageal varices. This finding underscores the potential of bSWE not merely as a diagnostic tool but as a powerful predictive measure that could impact clinical decisions regarding the management of these patients. With its ability to stratify risk quickly, bSWE emerges as a valuable adjunct to existing protocols.
The clinical implications of this study are crucial as they suggest that bSWE could assist in monitoring disease progression over time. Since portal hypertension can evolve and escalate in severity, having a reliable, non-invasive method to track these changes can significantly influence treatment strategies. Regular monitoring through bSWE could potentially reduce the frequency of invasive procedures, enhancing the quality of life for pediatric patients facing these serious health challenges.
Moreover, the accessibility of ultrasound technology presents an additional benefit. Many medical facilities already possess ultrasound machines, making it easier for hospitals and clinics to integrate bSWE into routine practice. However, as with any emerging technology, proper training and standardized protocols will be essential to ensure consistency and accuracy in measurements. The study provides a comprehensive foundation for future research that may refine these techniques and expand the clinical utility of bSWE in various settings.
Furthermore, understanding the safety profile of bSWE is paramount. As an entirely non-invasive approach, it eliminates risks associated with anesthesia and invasive monitoring, which are often unfavored in pediatric populations. The study’s findings indicate a favorable safety margin, suggesting that parents and caregivers may feel more at ease when opting for this modern diagnostic method over traditional invasive techniques. This reassurance could pave the way for broader acceptance of new technologies in pediatric care.
In addition to enhancing diagnostics, the introduction of bSWE may also stimulate further research into the underlying mechanisms of portal hypertension in children. As clinicians apply this technique in practice, they may uncover additional correlations between splenic stiffness and various clinical, biochemical, or histopathological markers. Such discoveries could deepen our understanding of pediatric portal hypertension and lead to the development of novel therapeutic strategies tailored to this vulnerable population.
Additionally, as the medical community continues to evolve, it is vital to explore pathways for curriculum integration. Incorporating bSWE into medical education and training allows future healthcare providers to become proficient in cutting-edge diagnostic technology, preparing them to better manage conditions like portal hypertension. Engaging early career clinicians in this dialogue may also lead to innovative research endeavors and collaborations that further advance the field.
The urgency surrounding advancements in technology for the diagnosis and management of pediatric portal hypertension cannot be overstated. The innovative work conducted by Mackintosh and colleagues emphasizes the importance of finding effective and safe modalities that facilitate better healthcare access for children. By embracing these new methodologies, the medical community stands to improve not only the standard of care but also the overall patient experience during critical moments.
In conclusion, this pivotal research on bidimensional shear wave elastography for diagnosing esophageal varices in children with portal hypertension represents a significant leap forward in pediatric imaging. With its potential to enhance diagnostic accuracy while ensuring patient safety, bSWE could soon become a mainstay in clinical practice, thereby offering hope and improved outcomes for children afflicted with this challenging condition. As the field of medical imaging evolves, there remains immense potential to uncover new insights and refine diagnostic practices that center around patient well-being.
As this research continues to gather attention, it sets the stage for future investigations that could further define the role of elastography across various pathologies and age groups. The commitment to exploring innovative approaches in the diagnosis of pediatric diseases reflects the ongoing efforts of researchers and clinicians to deliver comprehensive and compassionate care to those in need.
Subject of Research: Bidimensional shear wave spleen elastography for diagnosing and grading esophageal varices in pediatric patients with portal hypertension.
Article Title: Bidimensional shear wave spleen elastography for diagnosis and grading of esophageal varices in children with portal hypertension.
Article References: Mackintosh, C., Kaplan, J., Prati, A. et al. Bidimensional shear wave spleen elastography for diagnosis and grading of esophageal varices in children with portal hypertension. Pediatr Radiol (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-025-06351-x
Image Credits: AI Generated
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-025-06351-x
Keywords: Esophageal varices, portal hypertension, bidimensional shear wave elastography, pediatric radiology, non-invasive diagnostics.