Climate change is transforming dust storms—a natural phenomenon in the Middle East—into a more frequent and widespread threat to health and economies throughout the region, a new study shows.

Credit: KTH Royal Institute of Technology
Climate change is transforming dust storms—a natural phenomenon in the Middle East—into a more frequent and widespread threat to health and economies throughout the region, a new study shows.
Dust levels have increased in many parts of the Middle East chiefly due to global warming, but other human activities also share credit, says Zahra Kalantari, associate professor at KTH Royal Institute of Technology. She cites such factors as oil extraction, military conflicts and lack of cross-border coordination of water management.
Published in the journal Science of the Total Environment, the study maps the spread of aerosolized dust, and pinpoints where and when trends in precipitation and evaporation have changed course for the worse.
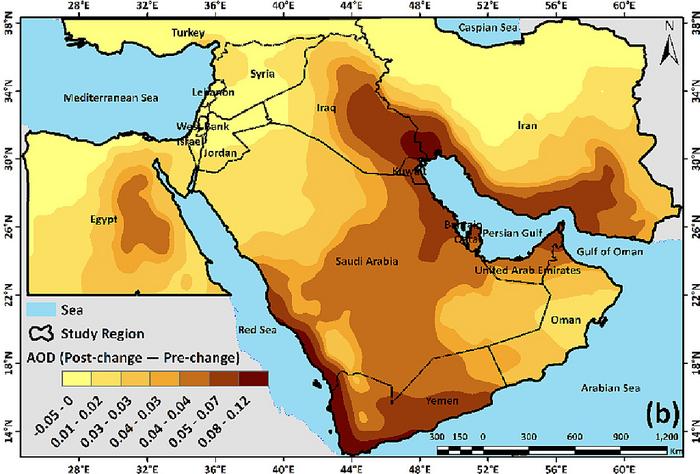
Analyzing multiple sets of data over the last 40 years, the researchers found an increase in dust levels in Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Yemen, parts of Iran and Egypt and countries around the Persian Gulf, while it has declined in northern Iran and southwest Turkey.
The area between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers in northern Iraq and along the Syria-Iraq border was reported to have the highest concentration of dust sources in the region, reflecting a sharp increase over the last 20 years.
The researchers documented a notable decrease in precipitation in northern Iraq, Syria, southwestern Iran, and southern Turkey. The natural effects of the area’s arid and hot climate have also been intensified by factors such as deforestation, dam building, over-irrigation and extraction of water and military conflict. Kalantari says one serious result is the reduction of soil moisture and vegetation coverage, which normally help reduce dust levels.
The environmental consequences include soil erosion, biodiversity loss and desertification, she says. Economic losses may result from damaged infrastructure, disrupted agriculture and reduced tourism.
Social disruption also can be expected, she says, and vulnerable populations will suffer disproportionately.
Kalantari says regional cooperation is vital to address complex factors and implement effective dust control measures. Comprehensive strategies are imperative to mitigate adverse effects on health, ecology, and socio-economic development.
The researchers call for “a comprehensive strategy focusing on environmental management and policy reforms.” Prescriptive measures include: reforestation, soil conservation, water conservation, regional cooperation, sustainable urban planning, advanced monitoring systems, public awareness campaigns and climate adaptation measures.
“These efforts, combined with research and cross-border collaboration, are essential for a sustainable environment that is resilient to dust storms in the Middle East,” Kalantari says.
Journal
Science of The Total Environment
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Dust and climate interactions in the Middle East: Spatio-temporal analysis of aerosol optical depth and climatic variables
Article Publication Date
1-Jun-2024
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.