Carbon emissions associated with air travel to professional conferences make up a sizable fraction of the emissions produced by researchers in academia. Andrea Gokus, a McDonnell Center postdoctoral fellow in the Department of Physics in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, is advocating for a reduction of these emissions.

Credit: Gokus et al., 2024
Carbon emissions associated with air travel to professional conferences make up a sizable fraction of the emissions produced by researchers in academia. Andrea Gokus, a McDonnell Center postdoctoral fellow in the Department of Physics in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, is advocating for a reduction of these emissions.
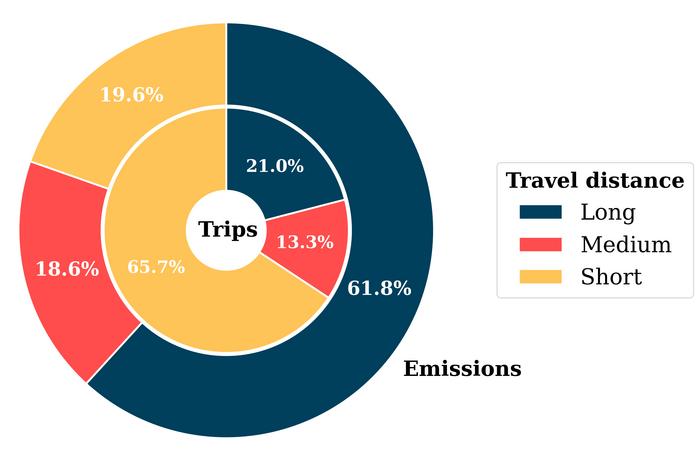
In a paper published in PNAS Nexus, Gokus and collaborators estimated the CO2-equivalent emissions for conference travel to all 362 open meetings in the field of astronomy in 2019.
The total is an estimated 42,500 tons, or about 1 ton per participant per meeting. But it doesn’t have to be that way.
“Networking and discussing new scientific developments at meetings is important for advancing the field, but adjustments can be made to reduce their hefty carbon cost,” Gokus said.
Via virtual meetings, the CO2-equivalent emissions due to travel can almost completely be eliminated. But such virtual offerings are often not regarded as efficient networking opportunities. Meeting organizers should consider preferentially locating conferences as close as possible to the majority of as many participants as possible, Gokus said, avoiding scenarios in which most are flying intercontinentally.
“My co-authors and I are all members of the grass-roots organization Astronomers for Planet Earth, or A4E,” said Gokus, who first became interested in sustainable astronomy during the annual meeting of the European Astronomical Society in 2020, which took place virtually due to the pandemic. “There are several other papers covering the emissions from particular meetings, including some recurring ones. But our paper is the first systematic study of all open meetings in an entire field.”
In addition to pure virtual meetings, Gokus and her co-authors propose hybrid formats and meetings held at a small number of physical hubs, which can then be virtually linked.
This approach has the potential to reduce long-haul (i.e., intercontinental) travel in particular, which contributes the majority of emissions. If intercontinental travel is unavoidable, the study authors suggest maximizing the time spent at the travel destination: by visiting the institutes of collaborators in the country, for example, and by choosing train or bus connections during such visits.
These choices not only make astronomy meetings greener, but they also can make astronomy more inclusive as a discipline, Gokus said. The researchers’ findings and suggestions could be applied to other academic disciplines as well.
Traveling to meetings is often more challenging for those from less-wealthy institutes; those farther from North American and European hubs; people who have to manage complex visa bureaucracies; researchers with disabilities; and those with caretaking responsibilities, she explained.
In her own space sciences research at WashU, Gokus focuses on the high-energy emission of active galactic nuclei, in particular blazars. She is interested in the processes occurring in their jets and studies their flux and spectral variability using instruments that cover the entire electromagnetic spectrum.
“What is great about making meetings more sustainable is that it can easily go hand in hand with making astronomy more inclusive as well,” Gokus said. “By making use of technology to connect virtually, we can foster a more inclusive collaborative approach, which can help us advance our understanding of the universe further. It is important that we work together as a community to achieve this goal, because there is no Planet B.”
Journal
PNAS Nexus
Article Title
Astronomy’s climate emissions: Global travel to scientific meetings in 2019
Article Publication Date
30-Apr-2024