“[…] intermittent ketogenic diet (IKD) or ketogenic diet (KD) intervention did not improve measures of cognitive or motor behavior in TgF344-AD rats; however, both IKD and KD positively impacted circulating lipids.”

Credit: 2024 Rutkowsky et al.
“[…] intermittent ketogenic diet (IKD) or ketogenic diet (KD) intervention did not improve measures of cognitive or motor behavior in TgF344-AD rats; however, both IKD and KD positively impacted circulating lipids.”
BUFFALO, NY- April 17, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 7, entitled, “The impact of continuous and intermittent ketogenic diets on cognitive behavior, motor function, and blood lipids in TgF344-AD rats.”
Studies suggest that ketogenic diets (KD) may improve memory in mouse models of aging and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). In this new study, researchers Jennifer M. Rutkowsky, Zabrisky Roland, Anthony Valenzuela, An B. Nguyen, Heui Hye Park, Natalie Six, Ilknur Dursun, Kyoungmi Kim, Pamela J. Lein, and Jon J. Ramsey from the University of California Davis and Istinye University determined whether a continuous or intermittent KD (IKD) enhanced cognitive behavior in the TgF344-AD rat model of AD.
“[…] it remains to be determined whether long-term consumption of a ketogenic diet can mitigate declines in cognitive or motor behavior in a rat model of AD. Therefore, the current study aimed to determine whether a KD improves cognitive or motor behavior in the TgF344-AD rat.”
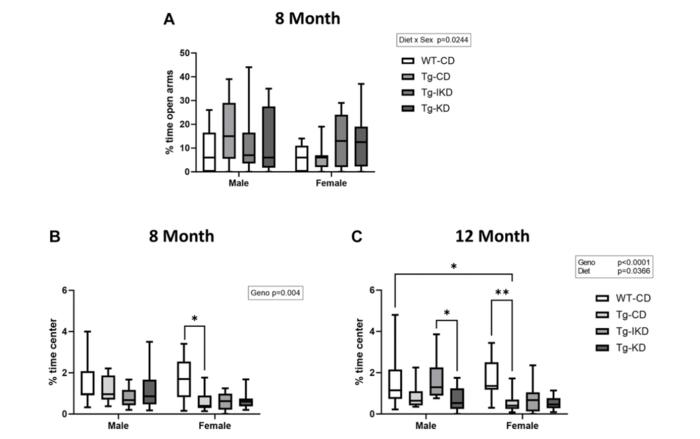
At 6 months-old, TgF344-AD and wild-type (WT) littermates were placed on a control (CD), KD, or IKD (morning CD and afternoon KD) provided as two meals per day for 2 or 6 months. Cognitive and motor behavior and circulating β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB), AD biomarkers and blood lipids were assessed. Animals on a KD diet had elevated circulating BHB, with IKD levels intermediate to CD and KD.
TgF344-AD rats displayed impaired spatial learning memory in the Barnes maze at 8 and 12 months of age and impaired motor coordination at 12 months of age. Neither KD nor IKD improved performance compared to CD. At 12 months of age, TgF344-AD animals had elevated blood lipids. IKD reduced lipids to WT levels with KD further reducing cholesterol below WT levels.
“[…] the IKD or KD did not improve motor coordination or spatial learning memory compared to the control diet. However, KD, and to a lesser extent IKD, mitigated elevations in plasma lipids in the TgF344-AD rats. Furthermore, the KD diet decreased plasma levels of total Tau in females.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205741
Corresponding Author: Jennifer M. Rutkowsky
Corresponding Email: jrutkowsky@ucdavis.edu
Keywords: ketogenic diet, Alzheimer’s disease, cognitive behavior, motor function, lipids
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Aging:
Aging publishes research papers in all fields of aging research including but not limited, aging from yeast to mammals, cellular senescence, age-related diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer’s diseases and their prevention and treatment, anti-aging strategies and drug development and especially the role of signal transduction pathways such as mTOR in aging and potential approaches to modulate these signaling pathways to extend lifespan. The journal aims to promote treatment of age-related diseases by slowing down aging, validation of anti-aging drugs by treating age-related diseases, prevention of cancer by inhibiting aging. Cancer and COVID-19 are age-related diseases.
Aging is indexed by PubMed/Medline (abbreviated as “Aging (Albany NY)”), PubMed Central, Web of Science: Science Citation Index Expanded (abbreviated as “Aging‐US” and listed in the Cell Biology and Geriatrics & Gerontology categories), Scopus (abbreviated as “Aging” and listed in the Cell Biology and Aging categories), Biological Abstracts, BIOSIS Previews, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
- X, formerly Twitter
- YouTube
- Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
Journal
Aging-US
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
The impact of continuous and intermittent ketogenic diets on cognitive behavior, motor function, and blood lipids in TgF344-AD rats
Article Publication Date
12-Apr-2024