The field of bone tissue engineering (BTE) was a promising avenue for addressing bone injuries and defects by constructing artificial scaffolds with bionic functionalities. Due to its unique 3D network structure, impressive mechanical properties, and excellent biocompatibility, BC has emerged as a captivating area of research in the realm of scaffold fabrication.

Credit: Co-Innovation Center for Efficient Processing and Utilization of Forest Resources, College of Chemical Engineering, Nanjing Forestry University, China, hcx@njfu.edu.cn
The field of bone tissue engineering (BTE) was a promising avenue for addressing bone injuries and defects by constructing artificial scaffolds with bionic functionalities. Due to its unique 3D network structure, impressive mechanical properties, and excellent biocompatibility, BC has emerged as a captivating area of research in the realm of scaffold fabrication.
The 3D printing was a precise technique for constructing intricate structures in damaged tissues or organs, which has been widely applied in bone tissue engineering field. However, the application of BC for 3D printing faces certain limitations that require attention, such as its dense 3D network structure, which impedes cellular penetration and weakens cell attachment. Besides, the tightly entangled fibers within BC may pose challenges for its extrusion as a bio-ink during the printing process, which will also limit the research has been conducted on the application of BC in 3D printing.
Maleic acid (MA) has emerged as a promising candidate for acid treatment of cellulose, primarily due to its eco-friendly nature and mild reaction conditions. In our previous work, it proved that MA solution with different concentration showed various effects on BC physicochemical properties and osteogenesis. While, the MA-mediated modification for BC was a kind of reversible reactions including ester reaction (forward reaction) and ester hydrolysis reaction (backward reaction). Hence, it is necessary to balance the volume of added MA solution in order to ensure the forward reaction for BC modification, which will gain deeper insights into the MA mediated modification process and unlock the full potential of modified BC in bone tissue engineering field.
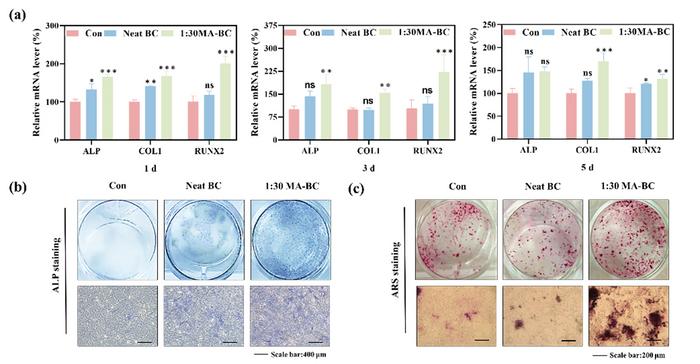
According to Xucai Wang, the investigator who led the study, this provides a new idea for the research of bacterial cellulose in bone tissue engineering. “The esterification process introduced carboxyl groups and hydrophobic properties to BC, thereby enhancing its suitability as a bio-ink for tissue engineering scaffolds. Additionally, the 1꞉30 MA-BC dispersion exhibited excellent biocompatibility, increased osteogenic gene expression, and increased mineralized nodule formation in vitro compared to the neat BC dispersion.” Also, the authors expect this work to provided valuable insights into the potential application of MA-BC dispersions in bone tissue engineering, particularly in facilitating proliferation and differentiation of osteocyte.
See the article:
DOI
Original Source URL
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S236996982400032X
Journal
Journal of Bioresources and Bioproducts
Journal
Journal of Bioresources and Bioproducts
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
Constructing Osteo-Inductive Bio-Ink for 3D Printing Through Hybridization of Gelatin with Maleic Acid Modified Bacterial Cellulose by Regulating Addition Volumes of Maleic Acid Solution
Article Publication Date
4-Apr-2024
COI Statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.