In a groundbreaking development that has significant implications for cardiac surgery practices, a recent unblinded randomized clinical trial has found that prothrombin complex concentrate (PCC) exhibits superior hemostatic efficacy compared to frozen plasma. This study addresses a critical need for effective coagulation factor replacement among patients experiencing bleeding during cardiac procedures. The findings from this trial could alter the landscape of transfusion practices, particularly in the context of surgical interventions where blood loss poses substantial risks.
Understanding the mechanism of action of PCC is pivotal in appreciating its advantages. Prothrombin complex concentrates contain a mixture of clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X, which are crucial in the coagulation cascade. This concentrated formulation allows for rapid restoration of hemostasis compared to frozen plasma, which requires time for thawing and administration. Given that patients undergoing cardiac surgery often experience significant blood loss, the ability to quickly restore coagulation is vital for surgical outcomes and patient safety.
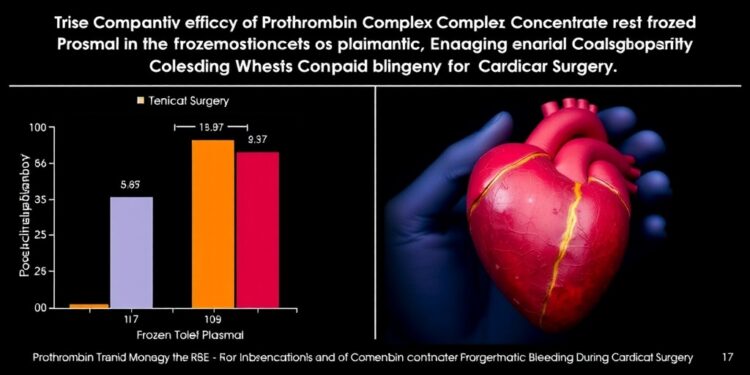
The trial specifically evaluated patients who required coagulation factor replacement due to bleeding during cardiac surgery. Participants receiving PCC demonstrated not only a faster response in achieving hemostasis but also reported fewer adverse effects compared to those treated with frozen plasma. The safety profile of PCC is particularly noteworthy, as it offers an alternative that minimizes the risk of transfusion-related complications, such as immune responses that can arise from exposure to multiple donor plasma.
Furthermore, the implications of these findings extend beyond immediate surgical environments. They suggest that PCC could become a first-line therapy for managing bleeding in various clinical situations, particularly those involving anticoagulated patients who require urgent surgical intervention. This adaptability could further influence clinical guidelines on the management of coagulopathies, potentially reducing the reliance on frozen plasma and its associated logistical challenges.
Notably, the study emphasizes the importance of a well-structured clinical approach when managing bleeding episodes. Enhanced protocols for the use of PCC could lead to improved patient outcomes post-surgery, minimizing morbidity related to hemorrhage. Implementing these protocols could significantly advance surgical care standards, ensuring that patients receive timely and effective treatment.
The research offers valuable insights not only into the effectiveness of PCC but also into the evolving field of hemostatic therapies. As surgical techniques advance, so too must our methods of managing complications such as bleeding. The findings serve as a call to action for further studies exploring the optimal application of PCC in various surgical contexts and for different patient populations.
The rigorous nature of the study and the strong data supporting its conclusions lend credibility to the findings. The unblinded design allows for a clearer understanding of treatment effects as clinicians and patients engaged fully in the trial. The data collected underlines the necessity for ongoing dialogue within the medical community about the efficacy of current standard practices and the potential benefits of adopting innovative therapies like PCC.
Importantly, dissemination of these findings is crucial. The study is set to be presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session, showcasing its relevance and potential impact on cardiovascular medicine. Engaging with broader medical audiences, including clinicians and policymakers, will be essential for translating research outcomes into clinical practice.
The role of prothrombin complex concentrate is consistent with a broader trend towards personalized medicine, where treatment approaches are tailored to individual patient needs. Identifying patients most likely to benefit from PCC can streamline care and enhance recovery trajectories, ultimately improving surgical outcomes and patient satisfaction.
As healthcare professionals continue to refine practices surrounding coagulation management, the adoption of PCC could represent a significant advance in clinical decision-making. Training and educating healthcare teams on the use of PCC will play a crucial role in ensuring its successful implementation in surgical settings and beyond.
In summary, the unblinded randomized clinical trial substantiates the hemostatic advantages of prothrombin complex concentrate over frozen plasma in the context of cardiac surgery. The findings not only highlight a vital alternative for managing surgical bleeding but also open the door for enhanced therapeutic strategies aimed at optimizing patient care and outcomes.
The effective incorporation of PCC into surgical protocols could redefine transfusion practices and represent a significant advancement in managing patients with bleeding complications. This study marks a significant step toward improving surgical practices and outcomes, affirming the value of ongoing clinical research in shaping future healthcare innovations.
Subject of Research: Prothrombin Complex Concentrate in Cardiac Surgery
Article Title: Superior Efficacy of Prothrombin Complex Concentrate Over Frozen Plasma in Surgical Bleeding
News Publication Date: Not specified
Web References: Not provided
References: Not provided
Image Credits: Not provided
Keywords: Prothrombin complex concentrate, frozen plasma, cardiac surgery, hemostasis, coagulation factors, clinical trial, transfusion practices, surgical outcomes, patient safety, bleeding complications, personalized medicine, healthcare innovation.