It’s interesting to hear about the research led by Minyi Guo that was published in Frontiers of Computer Science on 12 Mar 2024. It seems like they are addressing the challenge of reducing storage overhead in blockchain systems while maintaining data consistency and tolerating malicious nodes.

Credit: Mizhipeng ZHANG, Chentao WU, Jie LI, Minyi GUO
It’s interesting to hear about the research led by Minyi Guo that was published in Frontiers of Computer Science on 12 Mar 2024. It seems like they are addressing the challenge of reducing storage overhead in blockchain systems while maintaining data consistency and tolerating malicious nodes.
In traditional blockchain networks, full replication is used, where each node stores a complete copy of all blocks, and data consistency is maintained through a consensus protocol. However, this approach can be storage-intensive, especially as the blockchain grows over time.
To address this issue, previous approaches like BFT-Store and Partition Chain have used erasure codes to store blocks more efficiently. Erasure coding allows for data to be broken into smaller fragments, with redundant parities added, and distributed across multiple nodes. This reduces storage requirements and can help tolerate node failures.
The research team’s contribution appears to be in dynamically adjusting the encoding schema to tolerate malicious nodes more efficiently. They’ve observed that in typical cases, the number of malicious nodes is smaller than the threshold used for erasure coding. By dynamically adapting the encoding schema based on the actual number of malicious nodes, they aim to reduce unnecessary storage overhead associated with maintaining redundant parities to tolerate a larger number of malicious nodes than needed.
This research could have implications for improving the efficiency and scalability of blockchain networks, which is an important area of study as blockchain technology continues to evolve and find applications in various fields.
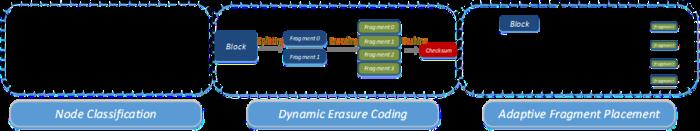
The team proposed a dynamic erasure coding method in permissioned blockchain systems called Dynamic-EC. The key idea of Dynamic-EC is to reduce the storage overhead by dynamically adjusting the total number of parities according to the risk level of the whole system, which is determined by the number of perceived malicious nodes, while ensuring the system reliability. Dynamic-EC can be divided into three modules: 1) Node Classification: this module is used to evaluate the global reputation value of each node. According to the reputation value, the nodes are classified into three categories: honest nodes, risk nodes and malicious nodes. 2) Dynamic Erasure Coding: this module is responsible for encoding the blocks into fragments and calculating the corresponding checksums in the leader node. The encoding schema is adaptively adjusted according to the current risk level of the system which is determined by the current number of risk nodes. 3) Adaptive Fragment Placement: this module distributes the encoded fragments from the leader node to the follower nodes.
Journal
Frontiers of Computer Science
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Dynamic-EC: an efficient dynamic erasure coding method for permissioned blockchain systems
Article Publication Date
12-Mar-2024