In recent years, cardiovascular diseases have emerged as a formidable public health challenge, necessitating the development of innovative diagnostic tools that facilitate early detection and intervention. The global burden of heart-related ailments has galvanized researchers and medical professionals to explore new frontiers in cardiac care, emphasizing the need for continuous, non-invasive monitoring methods. Among the most promising advancements in this field are wearable heart sound devices, which utilize cutting-edge technology to deliver real-time insights into heart health. These remarkable innovations mark a significant departure from traditional diagnostic tools, offering the potential to revolutionize the management of cardiovascular conditions.
Wearable heart sound devices leverage advanced sensor technology, allowing for persistent and accurate monitoring of heart sounds. Unlike conventional stethoscopes, which rely on periodic assessments, these devices can continuously track cardiac activity throughout a patient’s daily life. This unprecedented level of monitoring not only enhances clinical understanding but also empowers individuals to take an active role in managing their heart health. The ability to collect and analyze heart sound data in real-time opens up new avenues for personalized healthcare and remote patient monitoring, thereby improving patient outcomes and enhancing the overall effectiveness of cardiovascular disease management.
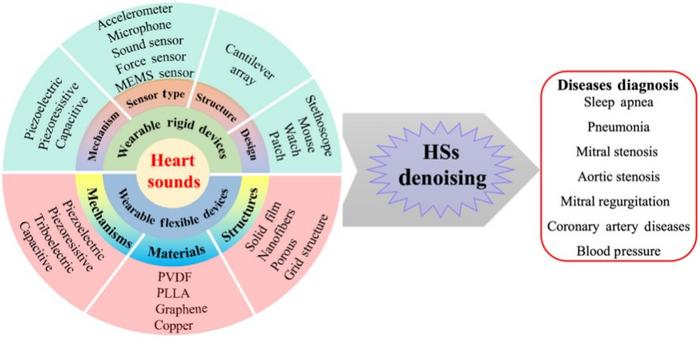
One of the notable features of these wearable devices is their design. Researchers have developed mechanoacoustic sensors that are notably soft and flexible, prioritizing user comfort while preserving optimal sensitivity and specificity. This engineering innovation is crucial in encouraging adherence to long-term monitoring regimens, as uncomfortable devices may deter patients from consistent usage. Additionally, the incorporation of advanced materials into the sensor designs allows for greater accuracy in detecting subtle changes in heart sounds, ultimately leading to more precise diagnostics.
Challenges remain, however, in the widespread adoption of wearable heart sound devices. Key issues such as sensitivity to noise, data accuracy, and user comfort must be addressed to ensure these devices reach their full potential in clinical settings. Moreover, the varying cardiac characteristics among individuals necessitate the ongoing refinement of these tools to accommodate diverse physiological differences. Confronting these challenges requires a concerted effort from researchers, engineers, and healthcare providers to collaborate on advancing the technology further.
Recent research conducted by scientists at the City University of Hong Kong sheds light on the latest advancements in this area. Their study published in the journal SmartMat provides an extensive review of wearable heart sound devices, highlighting the essential innovations that have paved the way for these remarkable tools. The research delves into various sensor types, materials utilized in device fabrication, and clinical applications, showcasing how multifaceted approaches can address traditional barriers in cardiac health monitoring.
Denoising techniques also play a pivotal role in enhancing the quality of heart sound analysis. Given the low-frequency nature of cardiac sounds, they can easily be obscured by environmental noise. The development of sophisticated algorithms capable of filtering out background interference represents a transformative leap in the ability to accurately analyze heart sounds. This innovation is crucial because accurate heart sound interpretation is essential for diagnosing conditions such as arrhythmias, valvular heart diseases, and other cardiovascular disorders.
As wearable technology continues to evolve, its integration into clinical practices holds the promise of redefining patient care paradigms. The potential applications of these devices are boundless, paving the way for innovative strategies in healthcare delivery. Remote monitoring capabilities can facilitate timely interventions based on real-time data, offering healthcare providers critical insights for informed decision-making. This approach not only promises to enhance the accuracy of diagnoses but also fosters a proactive engagement between patients and healthcare professionals.
The implications of such research extend beyond clinical diagnostics, potentially transforming public health strategies on a global scale. Increased access to wearable devices may democratize heart health information, allowing more individuals to monitor their conditions and take preventive measures. This shift towards a more engaged approach to cardiovascular disease management can significantly reduce the incidence of major adverse cardiac events, ultimately improving lifespans and quality of life for patients affected by heart diseases.
In conclusion, the evolution of wearable heart sound devices signifies a monumental advancement in the landscape of cardiovascular care. As researchers at the City University of Hong Kong and others continue to push the boundaries of technology, the promise of personalized, data-driven healthcare becomes increasingly tangible. These innovations not only have the potential to enhance clinical outcomes but also to empower patients to take charge of their health, radically transforming the narrative surrounding cardiovascular disease management.
The progress witnessed in the realm of wearable heart sound devices is a testament to the ingenuity and dedication of researchers committed to improving heart health. With continued exploration and development, it is anticipated that these devices will play an integral role in ushering in a new era of cardiac care, characterized by greater accessibility, improved accuracy, and enhanced patient engagement.
Moreover, as advancements in this technology gain momentum, the dialogue surrounding cardiovascular health will inevitably shift, not only within medical circles but among the general public. The increased acceptance of wearable health monitoring technologies can herald a new chapter in preventive healthcare and contribute significantly to the reduction of cardiovascular mortality rates worldwide. In this transformative age, the convergence of technology and healthcare reveals a future filled with promise, where patients and providers alike benefit from enhanced capabilities in heart health management.
Subject of Research: Wearable heart sound devices for cardiovascular monitoring
Article Title: Advancements in wearable heart sounds devices for the monitoring of cardiovascular diseases
News Publication Date: 26-Nov-2024
Web References: Link to SmartMat
References: DOI: 10.1002/smm2.1311
Image Credits: SmartMat
Keywords: Wearable devices, cardiovascular health, real-time monitoring, mechanoacoustic sensors, heart sound analysis