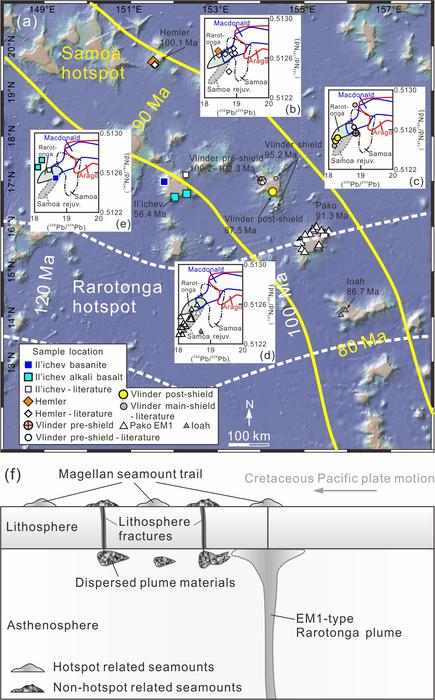
This study was led by Drs. Xun Wei and Xue-Fa Shi from the First Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resources, China. The researchers presented 40Ar-39Ar age, geochemical, and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopic data of lavas from Hemler, Vlinder, and Il’ichev seamounts in the West Pacific, to elucidate their petrogenesis and geodynamic process.

Credit: ©Science China Press
This study was led by Drs. Xun Wei and Xue-Fa Shi from the First Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resources, China. The researchers presented 40Ar-39Ar age, geochemical, and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopic data of lavas from Hemler, Vlinder, and Il’ichev seamounts in the West Pacific, to elucidate their petrogenesis and geodynamic process.
Oceanic intraplate volcanoes with linear age progressions are usually accepted to be derived from melting of an upwelling mantle plume. Many seamount groups, however, show complex age-distance relationship that are difficult to explain using the classic “mantle plume hypothesis”, and thus their origins are controversial. New 40Ar-39Ar age data of lavas from Hemler, Vlinder, and Il’ichev seamounts in the West Pacific do not lie on the old tracks of Macdonald, Arago, Rarotonga, and Samoa hotspots. They, however, have similar Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopic compositions to Rarotonga and Samoa plumes. The researchers proposed that in the mid-Cretaceous, when the Pacific plate passed over Rarotonga hotspot, melting of Rarotonga plume formed the Vlinder (main-shield stage), Pako, and Ioah seamounts. The Rarotonga (and possibly Samoa) plume materials would have been dispersed into the surrounding asthenosphere by mantle convection. These diffuse plume materials would undergo decompression melting beneath lithosphere fractures that are widely distributed in the Magellan area, generating non-hotspot related Hemler, pre- and post-shield Vlinder, and Il’ichev lavas.
This study indicates that hotspot volcanic rejuvenation along pre-existing fracture zones that caused melting of diffuse plume materials beneath the mid-Cretaceous lithosphere, and preferential channeling of magmas through pre-existing structural weaknesses or volcanic conduits together control the complex age-spatial-geochemical relationships of seamounts with plume-like compositional signatures in the West Pacific.
See the article:
Wei X, Zhang Y, Shi X, Zhang H. 2024. Geochronological and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis and geodynamic process of Hemler, Vlinder, and Il’ichev seamount lavas in NW Pacific. Science China Earth Sciences, 67(6): 1856–1871,
Journal
Science China Earth Sciences