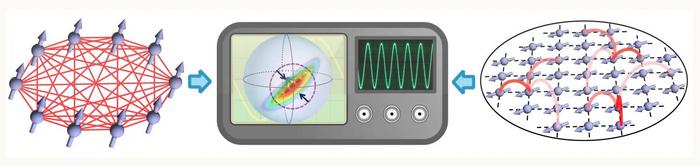
Nothing in science can be achieved or understood without measurement. Today, thanks to advances in quantum sensing, scientists can measure things that were once impossible to even imagine: vibrations of atoms, properties of individual photons, fluctuations associated with gravitational waves.

Credit: Bingtian Ye
Nothing in science can be achieved or understood without measurement. Today, thanks to advances in quantum sensing, scientists can measure things that were once impossible to even imagine: vibrations of atoms, properties of individual photons, fluctuations associated with gravitational waves.
A quantum mechanical trick called “spin squeezing” is widely recognized to hold promise for supercharging the capabilities of the world’s most precise quantum sensors, but it’s been notoriously difficult to achieve. In new research, Harvard physicists describe how they’ve put spin squeezing within better reach.
A type of quantum entanglement, spin squeezing constrains the way an ensemble of particles can fluctuate. This enables more precise measurements of certain observable signals, at the expense of measuring other, complementary signals as accurately — think of how squeezing a balloon yields more height at the expense of width.
“Quantum mechanics can enhance our ability to measure very small signals,” said Norman Yao, a physics professor and author of the new paper on spin squeezing in Nature Physics. “We have shown that it is possible to get such quantum-enhanced metrology in a much broader class of systems than was previously thought.”
In the balloon metaphor, a circle represents the uncertainty intrinsic to any quantum measurement, explained Maxwell Block, co-author of the paper and a former Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences student. “By squeezing this uncertainty, making the balloon more like an ellipse, one can reshape the sensitivity of measurements,” Block said. “This means that certain measurements can be more precise than anything one could possibly do without quantum mechanics.”
An analog of spin squeezing was used, for example, to increase the sensitivity of the Nobel-garnering gravitational wave detectors in the LIGO experiment.
The Harvard team’s work built upon a landmark 1993 paper that first described the possibility of a spin-squeezed, entangled state brought about by “all-to-all” interactions between atoms. Such interactions are akin to a large Zoom meeting, in which each participant is interacting with every other participant at once. Between atoms, this type of connectivity easily enables the build-up of the quantum mechanical correlations necessary to induce a spin-squeezed state. However, in nature, atoms typically interact in a way that’s more like a game of telephone, only speaking with a few neighbors at a time.
“For years, it has been thought that one can only get truly quantum-enhanced spin squeezing via all-to-all interactions,” said Bingtian Ye, co-lead author of the paper and also a former Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences student. “But what we have shown is that it is actually way easier.”
In their paper, the researchers outline a new strategy for generating spin-squeezed entanglement. They intuited, and together with collaborators in France quickly confirmed via experiment that the ingredients for spin squeezing are present in a ubiquitous type of magnetism found often in nature — ferromagnetism, which is also the force that makes refrigerator magnets stick. They posit that all-to-all interactions are not necessary to achieve spin squeezing, but rather, so long as the spins are connected well enough to sync into a magnetic state, they should also be able to dynamically generate spin squeezing.
The researchers are optimistic that by thus lowering the barrier to spin squeezing, their work will inspire new ways for quantum scientists and engineers to create more portable sensors, useful in biomedical imaging, atomic clocks, and more.
In that spirit, Yao is now leading experiments to generate spin-squeezing in quantum sensors made out of nitrogen-vacancy centers, which are a type of defect in the crystal structure of diamond that have long been recognized as ideal quantum sensors.
The research received federal support from: the Army Research Office, the Office of Naval Research, the Department of Energy, the Department of Defense, and the National Science Foundation.
Journal
Nature Physics
Method of Research
Computational simulation/modeling
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Scalable spin squeezing from finite-temperature easy-plane magnetism
Article Publication Date
29-Jul-2024