□ A team led by Professor Ji-woong Yang of DGIST’s (President Kun-woo Lee) Department of Energy Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Moon-kee Choi of UNIST’s Department of New Materials and Dr. Taeg-hwan Hyun of the IBS Nanoparticle Research Center, has developed a double-layer dry transfer printing technology that simultaneously transfers light-emitting and electron-transferring layers onto a substrate. This technology is expected to provide a more life-like view in augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), greatly enhancing the immersive experience.

Credit: A research conceptual diagram
□ A team led by Professor Ji-woong Yang of DGIST’s (President Kun-woo Lee) Department of Energy Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Moon-kee Choi of UNIST’s Department of New Materials and Dr. Taeg-hwan Hyun of the IBS Nanoparticle Research Center, has developed a double-layer dry transfer printing technology that simultaneously transfers light-emitting and electron-transferring layers onto a substrate. This technology is expected to provide a more life-like view in augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), greatly enhancing the immersive experience.
□ Recent advances in wearable, mobile, and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies are driving demand for AR, VR, and wearable displays. Wearable displays on the wrist or eyes need to convey large amounts of information on a small screen and require ultrahigh-definition patterning to prevent dizziness while wearing them.
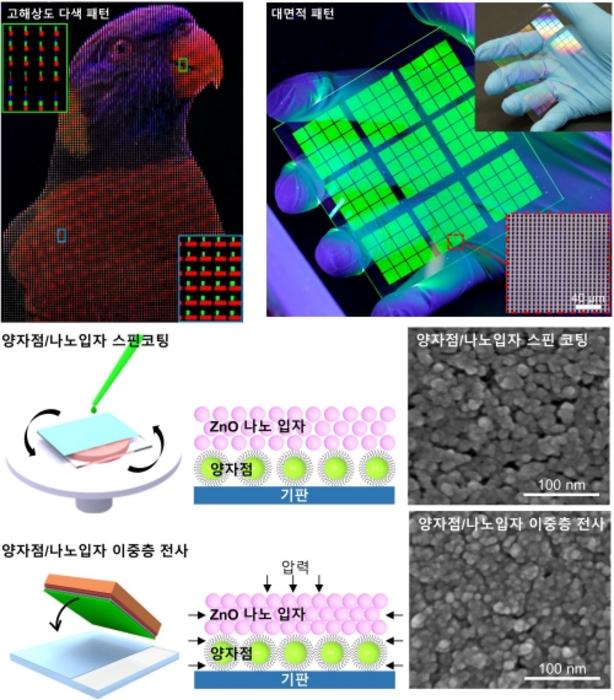
□ Quantum dot nanoparticles are emerging as the next generation of display light-emitting materials due to their high color purity and reproduction. However, conventional dry transfer printing, which involves applying quantum dot ink to a substrate, is capable of realizing ultrahigh-definition pixels but has not been used for actual display production due to its low luminescence efficiency of under 5%.
□ In this context, DGIST Professor Ji-woong Yang collaborated with UNIST Professor Moon-kee Choi and IBS Director Taeg-hwan Hyun to develop a dry transfer printing technology that can produce bright light even with low current. This enables high-resolution pixel patterning technology and creates light-emitting devices with ultrahigh-definition and high efficiency.
□ The new high-density double-layer thin films exhibit high external quantum efficiency (EQE) of up to 23.3% by reducing interfacial resistance, which facilitates electron injection and controls leakage charge transport in the fabrication of light-emitting devices. This is similar to the maximum theoretical efficiency of quantum dot light-emitting devices. The researchers also used the new thin film to create ultrahigh-definition patterns of quantum dots up to 25,526 PPI and achieved an 8 cm x 8 cm area through repeated printing, confirming the feasibility of mass production for product commercialization.
□ “By using double-layer dry transfer printing technology to reduce interfacial resistance and facilitate electron injection, we have fabricated light-emitting devices that are simultaneously ultrahigh-definition and high efficiency,” said Professor Ji-woong Yang of DGIST. “The light-emitting devices with double-layer thin films fabricated using this technology exhibited high EQE of up to 23.3%, similar to the maximum theoretical efficiency of quantum dot light-emitting devices, which is a very significant result.”
□ “We are pleased to have developed a technology that enables higher resolution screens in VR and AR through this research,” said UNIST Professor Moon-kee Choi. “Through further research, we will strive to broadly apply quantum dots with high color reproduction and color purity to smart wearable devices.”
□ The research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea and the Samsung Future Technology Development Program, among others, and was published online in August in Nature Photonics, the world’s leading international journal in the field of optics.
– Corresponding Author E-mail Address : jiwoongyang@dgist.ac.kr