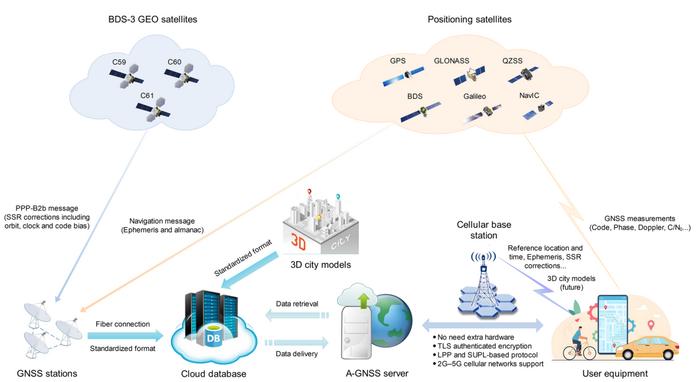
The latest advancements in smartphone positioning technology were put to the test in a recent study. Focusing on the multi-frequency Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) capabilities of the Redmi K60 Ultra, the study evaluated performance across various scenarios, demonstrating significant improvements in positioning accuracy, speed, and reliability. These developments mark a crucial step forward in high-precision positioning for consumer devices, leveraging Assisted GNSS (A-GNSS) services to enhance everyday navigation experiences.
Smartphone positioning technologies have evolved rapidly, with increasing demands for precision in urban environments where signal obstructions are common. Traditional Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) methods, while effective in open areas, often struggle in dense cityscapes due to signal interference and multipath errors. Addressing these challenges is crucial for improving navigation and location-based services, which are integral to modern life. Based on these challenges, it is necessary to conduct in-depth research on the performance of multi-frequency GNSS in smartphones.
In August 2023, Xiaomi launched the Redmi K60 Ultra, the first smartphone to integrate BeiDou-3 Navigation Satellite System Precise Point Positioning (PPP-B2b) services. The study (DOI: 10.1186/s43020-024-00146-5), published in Satellite Navigation, in 2024, conducted a comprehensive performance evaluation of this multi-frequency GNSS smartphone. Researchers from Beihang University, the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology and other institutions tested the device under various conditions, revealing its advanced capabilities in enhancing GNSS-based positioning.
The study evaluated the Redmi K60 Ultra’s multi-frequency GNSS capabilities across six diverse scenarios, including lab tests and urban environments. Results showed significant improvements in positioning accuracy and speed, driven by the A-GNSS PPP-B2b service. The smartphone reduced the Time to First Fix (TTFF) by over 85% during cold starts, achieving accuracy within 1.5 meters in open-sky conditions. In urban areas, where signal obstructions are common, the integration of the 3DMA GNSS algorithm further enhanced positioning accuracy by over 30%. These findings demonstrate the Redmi K60 Ultra’s leading role in consumer GNSS technology, offering reliable and precise navigation even in complex settings. The device sets a new standard for smartphone-based high-precision positioning, with broad implications for everyday and specialized applications.
Dr. Fu Zheng, one of the lead researchers, stated, “This study demonstrates the potential of multi-frequency GNSS in transforming smartphone positioning technology. The integration of A-GNSS services with advanced algorithms like 3DMA GNSS marks a significant leap in achieving high-precision positioning in challenging environments. These results pave the way for the next generation of smart devices that can deliver unprecedented accuracy in real-time navigation.”
The implications of this study extend beyond consumer navigation. The advancements in GNSS positioning could enhance applications in areas such as autonomous driving, augmented reality, and smart city infrastructure. As smartphones continue to integrate more sophisticated GNSS technologies, users can expect improved reliability and accuracy in location-based services, transforming how we interact with the world around us.

Credit: Satellite Navigation
The latest advancements in smartphone positioning technology were put to the test in a recent study. Focusing on the multi-frequency Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) capabilities of the Redmi K60 Ultra, the study evaluated performance across various scenarios, demonstrating significant improvements in positioning accuracy, speed, and reliability. These developments mark a crucial step forward in high-precision positioning for consumer devices, leveraging Assisted GNSS (A-GNSS) services to enhance everyday navigation experiences.
Smartphone positioning technologies have evolved rapidly, with increasing demands for precision in urban environments where signal obstructions are common. Traditional Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) methods, while effective in open areas, often struggle in dense cityscapes due to signal interference and multipath errors. Addressing these challenges is crucial for improving navigation and location-based services, which are integral to modern life. Based on these challenges, it is necessary to conduct in-depth research on the performance of multi-frequency GNSS in smartphones.
In August 2023, Xiaomi launched the Redmi K60 Ultra, the first smartphone to integrate BeiDou-3 Navigation Satellite System Precise Point Positioning (PPP-B2b) services. The study (DOI: 10.1186/s43020-024-00146-5), published in Satellite Navigation, in 2024, conducted a comprehensive performance evaluation of this multi-frequency GNSS smartphone. Researchers from Beihang University, the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology and other institutions tested the device under various conditions, revealing its advanced capabilities in enhancing GNSS-based positioning.
The study evaluated the Redmi K60 Ultra’s multi-frequency GNSS capabilities across six diverse scenarios, including lab tests and urban environments. Results showed significant improvements in positioning accuracy and speed, driven by the A-GNSS PPP-B2b service. The smartphone reduced the Time to First Fix (TTFF) by over 85% during cold starts, achieving accuracy within 1.5 meters in open-sky conditions. In urban areas, where signal obstructions are common, the integration of the 3DMA GNSS algorithm further enhanced positioning accuracy by over 30%. These findings demonstrate the Redmi K60 Ultra’s leading role in consumer GNSS technology, offering reliable and precise navigation even in complex settings. The device sets a new standard for smartphone-based high-precision positioning, with broad implications for everyday and specialized applications.
Dr. Fu Zheng, one of the lead researchers, stated, “This study demonstrates the potential of multi-frequency GNSS in transforming smartphone positioning technology. The integration of A-GNSS services with advanced algorithms like 3DMA GNSS marks a significant leap in achieving high-precision positioning in challenging environments. These results pave the way for the next generation of smart devices that can deliver unprecedented accuracy in real-time navigation.”
The implications of this study extend beyond consumer navigation. The advancements in GNSS positioning could enhance applications in areas such as autonomous driving, augmented reality, and smart city infrastructure. As smartphones continue to integrate more sophisticated GNSS technologies, users can expect improved reliability and accuracy in location-based services, transforming how we interact with the world around us.
###
References
DOI
Original Source URL
Funding information
This work was sponsored by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. YWF-23-JC-12), the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42004026), 03 Special and 5G Project of Jiangxi Province (Grant No. 20224ABC03W03), and Science and Technology Program of Yunnan Province (Grant No. 202102AE090051).
About Satellite Navigation
Satellite Navigation (E-ISSN: 2662-1363; ISSN: 2662-9291) is the official journal of Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The journal aims to report innovative ideas, new results or progress on the theoretical techniques and applications of satellite navigation. The journal welcomes original articles, reviews and commentaries.
Journal
Satellite Navigation
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Multi-frequency smartphone positioning performance evaluation: insights into A-GNSS PPP-B2b services and beyond
Article Publication Date
5-Aug-2024
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.