To control the climate crisis, we must tackle methane emissions now. Methane has contributed about half the global warming we’ve experienced so far, and emissions are climbing rapidly. An international team of climate researchers writing in Frontiers in Science set out three imperatives to cut methane emissions and share a new tool to help us find the most cost-effective ways of doing so.

Credit: Shindell D et al/Frontiers
To control the climate crisis, we must tackle methane emissions now. Methane has contributed about half the global warming we’ve experienced so far, and emissions are climbing rapidly. An international team of climate researchers writing in Frontiers in Science set out three imperatives to cut methane emissions and share a new tool to help us find the most cost-effective ways of doing so.
“The world has been rightly focused on carbon dioxide, which is the largest driver of climate change to date,” said Professor Drew Shindell of Duke University, lead author. “Methane seemed like something we could leave for later, but the world has warmed very rapidly over the past couple of decades, while we’ve failed to reduce our CO2 emissions. So that leaves us more desperate for ways to reduce the rate of warming rapidly, which methane can do.”
Reduce, coordinate, and incentivize
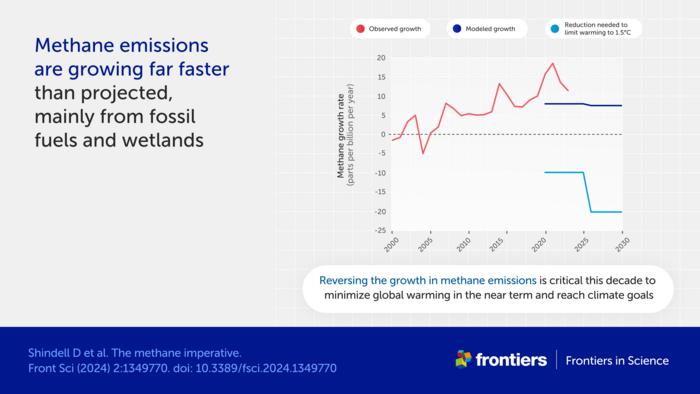
Methane is the second most potent greenhouse gas, but only about 2% of global climate finance goes towards cutting methane emissions. These emissions are also rising fast, due to a combination of emissions from fossil fuel production and increased emissions from wetlands, driven by the climate crisis. To slow the damage from climate change and make it possible to keep global warming below 2°C, we need to act immediately, following the Global Methane Pledge to reduce methane emissions by 30% from their 2020 level by 2030.
The scientists lay out three critical imperatives for action, backed by analyses of satellite remote sensing data, reported methane emissions, and the interaction of abatement options with market forces. Firstly, we need to bring methane emissions down. Secondly, we need to coordinate efforts to tackle methane and carbon dioxide emissions—only cutting carbon dioxide won’t stop warming quickly enough, but only cutting methane just delays global heating. Thirdly, we need to incentivize and enforce methane abatement.
This is a life-saving, cost-effective measure. Estimates indicate that every tonne of methane emitted in 2020 caused US$470-1700 of damages. But this may be a significant underestimate: taking into consideration the effect on air pollution that damages human health, the true cost could be up to $7,000 per tonne—and rising.
“The benefits of methane mitigation nearly always outweigh the net costs,” explained Shindell. “Many methane mitigation options provide net economic gains even without accounting for environmental impacts.”
Methane doesn’t accumulate in the atmosphere in the long term, so emissions reductions take effect more quickly. If we could cut all methane emissions tomorrow, in 30 years more than 90% of accumulated methane—but only around 25% of carbon dioxide—would have left the atmosphere.
“The most important mitigations are the available mitigation options across all sectors that aren’t too expensive, because we really need to do everything to reach climate targets such as 1.5 or 2C warming,” said Shindell. “Controlling methane from only one sector wouldn’t be enough. We need a broad portfolio of actions.”
The right tools for the job
The most impactful opportunities to fight methane will depend on the measures a country has already taken and the industries it relies on. So the authors created an online tool to identify the most effective measures for abatement in different countries. For big fossil fuel producers, regulating production, incentivizing the capture of methane, or charging companies for methane emissions could be the most effective options. For others, focusing on emissions from landfills could offer the biggest rewards. Individuals can help by making lifestyle changes and by thinking about the environment when they vote.
“People can make sure they avoid overconsumption of beef and dairy, and compost their organic waste whenever possible,” said Shindell. “If it’s not possible where they live, they can vote for those who’ll create programs for composting in their towns. They can also vote for those who will make polluters pay for methane emission rather than letting them profit while society picks up the tab for the damages they’re inflicting.”
“There are uncertainties, of course,” cautioned Shindell. “We don’t yet have enough data to fully parse out the contributions of individual factors to the recent surge in the observed growth rate, for example. But it is imperative to rapidly reduce methane emissions to reduce the accelerating climate damages so many people around the world are suffering.”
Journal
Frontiers in Science
Method of Research
Data/statistical analysis
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
The methane imperative
Article Publication Date
30-Jul-2024
COI Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer FOC declared a past co-authorship with the author SS to the handling editor.