Los Angeles, California – May 20, 2024 – Researchers at the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) have unveiled a pioneering study shedding light on the intricate mechanisms underlying Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The study, titled “Effects of amyloid-β-mimicking peptide hydrogel matrix on neuronal progenitor cell phenotype,” represents a significant leap forward in understanding the interplay between amyloid-like structures and neuronal cells.

Credit: Terasaki Institute
Los Angeles, California – May 20, 2024 – Researchers at the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) have unveiled a pioneering study shedding light on the intricate mechanisms underlying Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The study, titled “Effects of amyloid-β-mimicking peptide hydrogel matrix on neuronal progenitor cell phenotype,” represents a significant leap forward in understanding the interplay between amyloid-like structures and neuronal cells.
Led by Natashya Falcone and co-first authors Tess Grett Mathes and Mahsa Monirizad, the research team delved into the realm of self-assembling peptide-based hydrogels, renowned for their versatility in mimicking extracellular matrices (ECMs) of diverse microenvironments.
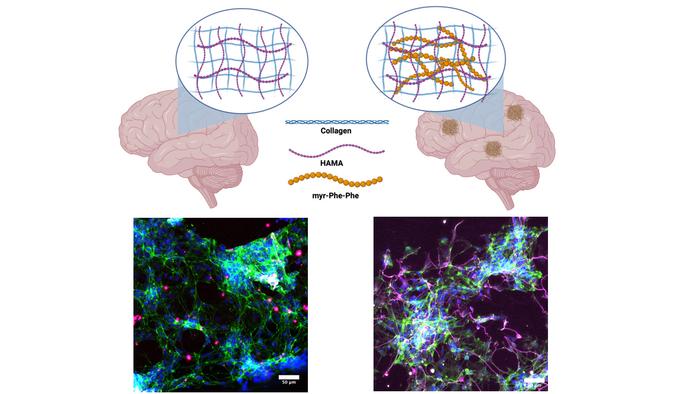
AD presents an intricate challenge in neurodegenerative research. Traditional two-dimensional (2D) models have limitations in capturing the complexity of the disease. Through their innovative approach, the team developed a multi-component hydrogel scaffold, named Col-HAMA-FF, designed to mimic the amyloid-beta (β) containing microenvironment associated with AD.
The study’s findings, published in a recent issue of Acta Biomaterialia, illuminate the formation of β-sheet structures within the hydrogel matrix, mimicking the nanostructures of amyloid-β proteins. By culturing healthy neuronal progenitor cells (NPCs) within this amyloid-mimicking environment and comparing results to those in a natural-mimicking matrix, the researchers observed elevated levels of neuroinflammation and apoptosis markers. This suggests a significant impact of amyloid-like structures on NPC phenotypes and behaviors.
Dr. Ali Khademhosseini, the study’s corresponding author, expressed excitement about the implications of their findings: “This foundational work provides a promising scaffold for future investigations into AD mechanisms and drug testing. By bridging the gap between 3D hydrogel models and the complex reality of AD pathological nanostructures, we aim to understand this interaction on healthy neuronal cells so that we can accelerate the development of effective therapeutic strategies.”
The study represents a crucial step towards unraveling the mysteries of the b-amyloid-like environment which can be found in AD and marks a milestone in the quest for innovative solutions to combat neurodegenerative disorders.
Authors: Tess Grett Mathes, Mahsa Monirizad, Menekse Ermis, Natan Roberto de Barros, Marco Rodriguez, Heinz-Bernhard Kraatz, Vadim Jucaud, Ali Khademhosseini, Natashya Falcone
###
Grant Information
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Institutes of Health (1R01DK130566-01, 1R01CA257558-01) and the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation, Los Angeles, CA. N.F. appreciates the postdoctoral fellowship (PDF) from the National Science and Engineering Research Council (NSERC).
About Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI):
The Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation is a non-profit research organization dedicated to leveraging cutting-edge technology to address global health challenges. By fostering interdisciplinary collaborations and pushing the boundaries of innovation, TIBI aims to transform healthcare and improve lives worldwide.
For more information, please contact:
Stewart Han
Email: shan@terasaki.org
Natashya Falcone, Ph.D.
Email: nfalcone@terasaki.org
Journal
Acta Biomaterialia
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Effects of amyloid-β-mimicking peptide hydrogel matrix on neuronal progenitor cell phenotype
Article Publication Date
25-May-2024