“[…] it is crucial for the future application of ABC transporter inhibitors […] to develop a stratification protocol […] to identify those PDAC patients who are most likely to benefit from chemosensitization induced by these inhibitors.”

Credit: 2024 Bergonzini et al.
“[…] it is crucial for the future application of ABC transporter inhibitors […] to develop a stratification protocol […] to identify those PDAC patients who are most likely to benefit from chemosensitization induced by these inhibitors.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 10, 2024 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncotarget’s Volume 15 on June 20, 2024, entitled, “Targeting ABC transporters in PDAC – past, present, or future?”
In this new editorial, Cecilia Bergonzini, Elisa Giovannetti and Erik H.J. Danen from Leiden University discuss targeting ABC transporters in pancreatic ductal carcinoma (PDAC). Despite its lower incidence as compared to more common cancers such as lung or breast carcinomas, PDAC ranks as the third leading cause of cancer mortality in the US and the sixth worldwide. This is due to the fact that PDAC survival rates are among the lowest for cancer patients, around 13% in the US.
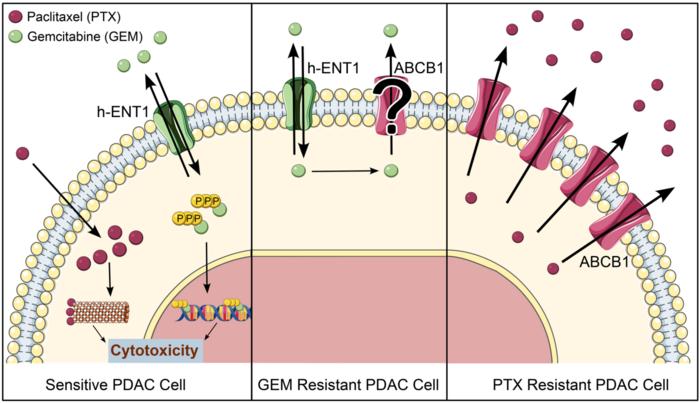
ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters represent a family of transmembrane proteins that, using the energy from ATP hydrolysis, extrude molecules from the cytoplasm to the exterior or into vesicles. Some of these transporters have been associated with resistance to a spectrum of structurally diverse chemotherapeutic drugs, earning them the name of multidrug resistance (MDR) pumps. One of the best-characterized ABC transporters is ABCB1 (MDR1). It is physiologically expressed in tissues such as kidney, liver, pancreas, intestine, the blood-brain barrier, and more, where it exerts a protective role, by extruding xenobiotics and potentially toxic molecules. Moreover, increased ABCB1 expression in tumors has been associated with poor prognosis.
“Paclitaxel is a bona fide substrate for ABCB1 [18] and ABCB1 has been implicated in paclitaxel and nab-paclitaxel resistance in multiple types of cancer [19, 20]. Could ABCB1 represent a therapeutic target in PDAC patients to suppress resistance against GnP? We have recently reported that ABCB1 can indeed play a critical role in paclitaxel resistance in PDAC cells [21].”
Continue reading: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28597
Correspondence to: Erik H.J. Danen
Email: e.danen@lacdr.leidenuniv.nl
Keywords: PDAC; chemoresistance; ABCB1
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
Oncotarget is indexed and archived by PubMed/Medline, PubMed Central, Scopus, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
- X, formerly Twitter
- YouTube
- Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Street., Suite 1
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
Journal
Oncotarget
Method of Research
Commentary/editorial
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Targeting ABC transporters in PDAC – past, present, or future?
Article Publication Date
20-Jun-2024