Individuals diagnosed with prediabetes can reduce their long-term risk of death and diabetes-related health complications if they delay the onset of diabetes for just four years through diet and exercise. Guangwei Li of the China-Japan Friendship Hospital and colleagues report these findings in a new study published July 9th in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine.

Credit: Xin Qian and Guangwei Li (CC-BY 4.0,
Individuals diagnosed with prediabetes can reduce their long-term risk of death and diabetes-related health complications if they delay the onset of diabetes for just four years through diet and exercise. Guangwei Li of the China-Japan Friendship Hospital and colleagues report these findings in a new study published July 9th in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine.
Type 2 diabetes is associated with an increased risk of death and disability, and imposes a significant economic burden on individuals and societies worldwide. Lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet and getting more exercise, can delay or reduce the risk of developing diabetes in people diagnosed with impaired glucose tolerance – commonly called prediabetes. However, it is unknown how long a person must delay diabetes to ensure better long-term health.
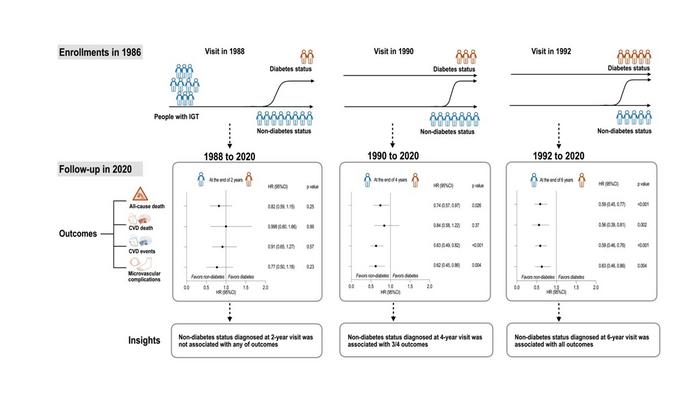
In the new study, researchers looked at health outcomes from 540 prediabetic individuals who participated in the original Da Qing Diabetes Prevention Study, a six-year trial conducted in Da Qing City in China, starting in 1986. Participants belonged to either a control group or one of three lifestyle intervention groups, which involved following a healthy diet, getting more exercise, or both. The trial followed up with participants for more than 30 years.
Li’s team determined the long-term risk of death, cardiovascular events – like heart attack, stroke or heart failure – and other diabetes-related complications for trial participants. They found that individuals who remained non-diabetic for at least four years after their initial diagnosis had a significantly lower risk of dying and a significantly lower risk of experiencing a cardiovascular event compared to those who developed diabetes sooner. This protective effect was not observed in individuals who remained non-diabetic for less than the “four-year threshold.”
Overall, the analysis suggests that the longer a prediabetic person can delay developing diabetes, the better their long-term health outcomes will be. However, even just a few years of maintaining prediabetic status can yield benefits for years to come.
The authors add, “This study suggests that a longer duration of non-diabetes status in those with IGT has beneficial health outcomes and reduces mortality. The implementation of effective interventions targeting those with IGT should be considered as part of preventative management for diabetes and diabetes related vascular complications.”
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Medicine:
Citation: Qian X, Wang J, Gong Q, An Y, Feng X, He S, et al. (2024) Non-diabetes status after diagnosis of impaired glucose tolerance and risk of long-term death and vascular complications: A post hoc analysis of the Da Qing Diabetes Prevention Outcome Study. PLoS Med 21(7): e1004419.
Author Countries: China
Funding: see manuscript
Journal
PLoS Medicine
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
People
COI Statement
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.