A research team of Professor Yoontae Lee and Jiho Park, a PhD candidate, from the Department of Life Sciences at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) recently discovered that a particular protein promotes the development of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The study was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS), one of the world’s most-cited multidisciplinary scientific journal.

Credit: POSTECH
A research team of Professor Yoontae Lee and Jiho Park, a PhD candidate, from the Department of Life Sciences at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) recently discovered that a particular protein promotes the development of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The study was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS), one of the world’s most-cited multidisciplinary scientific journal.
B cells, components of the body’s immune system, produce antibodies to combat pathogens such as viruses that enter the body from the outside. T follicular helper (TFH) cells assist B cells in generating these antibodies. However, an overabundance of TFHs can cause B cells to become overly active, resulting in autoimmune diseases. In such cases, B cells mistakenly recognize the body’s own tissues and cells as pathogens and produce autoantibodies even when no external pathogens are present.
SLE, one of the most prevalent autoimmune diseases, is marked by a butterfly-shaped red rash and arthritis that primarily affects the nose and cheeks. The symptoms and affected immune cells vary from patient to patient, and the cause and the underlying mechanisms are not clearly understood, complicating the provision of personalized treatment.
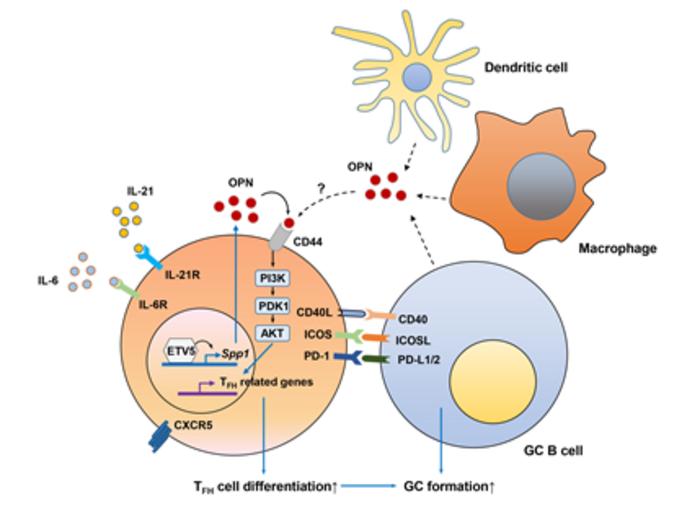
Previous research by Professor Yoontae Lee’s team suggested that ETV5, a specific transcription factor expressed in T cells, promotes the differentiation of T cells into TFH cells, potentially leading to SLE. In this study, the team conducted experiments in both mice and humans to confirm this hypothesis.
As a result, autoimmune symptoms such as autoantibody concentrations, immune cell infiltration into body tissues, and renal glomerulonephritis, and the development of TFH cells were reduced in the ETV5-deficient SLE mouse model. The team discovered that ETV5 enhances the expression of its target protein, osteopontin (OPN) which in turn activates the AKT protein, leading to the differentiation into TFH cells.
The researchers further confirmed that in human T cells, the differentiation into TFH cells is also regulated by the levels of ETV5 and OPN expression. Aligning with the findings from the animal models, ETV5 and OPN were expressed at higher levels in SLE patient models compared to the general population. Additionally, disease activity and blood autoantibody concentrations were generally proportional to the levels of ETV5 and OPN expression.
Professor Yoontae Lee, who led the study, expressed his aspiration by saying, “We have identified a mechanism of SLE pathogenesis involving ETV5 and OPN in real-world experiments.” He added, “We hope that further research will lead to the development of ETV5 inhibitors that regulate TFH cell development to help treat SLE patients.”
The research was conducted with support from the Mid-Career Research Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Journal
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Article Title
ETV5 promotes lupus pathogenesis and follicular helper T cell differentiation by inducing osteopontin expression
Article Publication Date
7-May-2024