“[…] the development of a global conceptual definition of sarcopenia signifies a new dawn for this muscle disease.”

Credit: 2024 Kirk et al.
“[…] the development of a global conceptual definition of sarcopenia signifies a new dawn for this muscle disease.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 26, 2024 – A new editorial paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 11, entitled, “Global consensus for sarcopenia.”
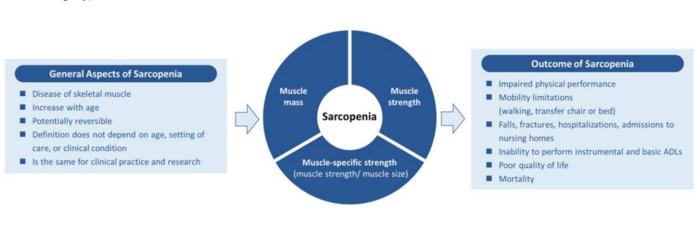
In this new editorial, researchers Ben Kirk, Peggy M. Cawthon, and Alfonso J. Cruz-Jentoft from the University of Melbourne and Western Health discuss the global societal issue of skeletal muscle loss and weakness, termed Sarcopenia. Low muscle mass or low strength/function increases the susceptibility to poor outcomes such as fragility, hip fractures, disability, and low quality of life in older people [1–4]. Skeletal muscle also acts as an endocrine organ and interacts with local and distal tissues; for instance, muscle cells secrete molecules involved in bone fracture healing and the same molecules help regulate distal tissues such as the brain, heart, and kidneys [5, 6]. This may partially explain why low muscle mass is a strong predictor of disease-specific mortality (dementia, cancer, heart failure, kidney/liver disease) as well as all-cause mortality in aging [7].
“Until now, there has been no universal agreement on a definition for Sarcopenia.”
Previous definitions were continent- and region-specific: Asia, Europe, North America, and Australia/New Zealand [8]. These definitions were certainly important in drawing attention to, and understanding of, this muscle disease. However, these definitions led to wide estimates in disease prevalence/incidence as well as heterogeneity when comparing treatments results of randomised trials [9]. The lack of a single definition likely impacted the identification of or treatment for sarcopenia in research and clinical practice (i.e., caused confusion for scientists, physicians and health care professionals on which definition, cutpoints, and muscle assessment tools to employ).
“To address this, the Global Leadership Initiative in Sarcopenia (GLIS) [9] was formed to create a unified global definition for use in research and clinical settings.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205919
Corresponding Author: Ben Kirk
Corresponding Email: ben.kirk@unimelb.edu.au
Keywords: sarcopenia, global definition, GLIS, skeletal muscle
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Aging:
The journal Aging aims to promote 1) treatment of age-related diseases by slowing down aging, 2) validation of anti-aging drugs by treating age-related diseases, and 3) prevention of cancer by inhibiting aging. (Cancer and COVID-19 are age-related diseases.)
Aging is indexed by PubMed/Medline (abbreviated as “Aging (Albany NY)”), PubMed Central, Web of Science: Science Citation Index Expanded (abbreviated as “Aging‐US” and listed in the Cell Biology and Geriatrics & Gerontology categories), Scopus (abbreviated as “Aging” and listed in the Cell Biology and Aging categories), Biological Abstracts, BIOSIS Previews, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
- X, formerly Twitter
- YouTube
- Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
Journal
Aging-US
Method of Research
Commentary/editorial
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Global consensus for sarcopenia
Article Publication Date
17-May-2024