Maternal immunity refers to the immunity transferred across the placenta, colostrum, milk or eggs from mother to offspring. It plays a key role in protecting the vulnerable offspring against pathogenic attacks, and is present in nearly all vertebrates and invertebrates. As one of the ancient vertebrates, teleost fish continuously secrete a substantial amount of mucus due to their unique living environment, and often exhibit schooling behavior. Previous studies have highlighted the presence of numerous immune components in the mucus of fish, which plays a crucial role in resisting pathogens.

Credit: Zixuan Wang
Maternal immunity refers to the immunity transferred across the placenta, colostrum, milk or eggs from mother to offspring. It plays a key role in protecting the vulnerable offspring against pathogenic attacks, and is present in nearly all vertebrates and invertebrates. As one of the ancient vertebrates, teleost fish continuously secrete a substantial amount of mucus due to their unique living environment, and often exhibit schooling behavior. Previous studies have highlighted the presence of numerous immune components in the mucus of fish, which plays a crucial role in resisting pathogens.
This information prompted a team of researchers in China to investigate whether adult fish mucus can serve as a form of maternal immunity in fish, and function as an immunomodulator during the larvae stage of their offspring when faced with pathogen threats.
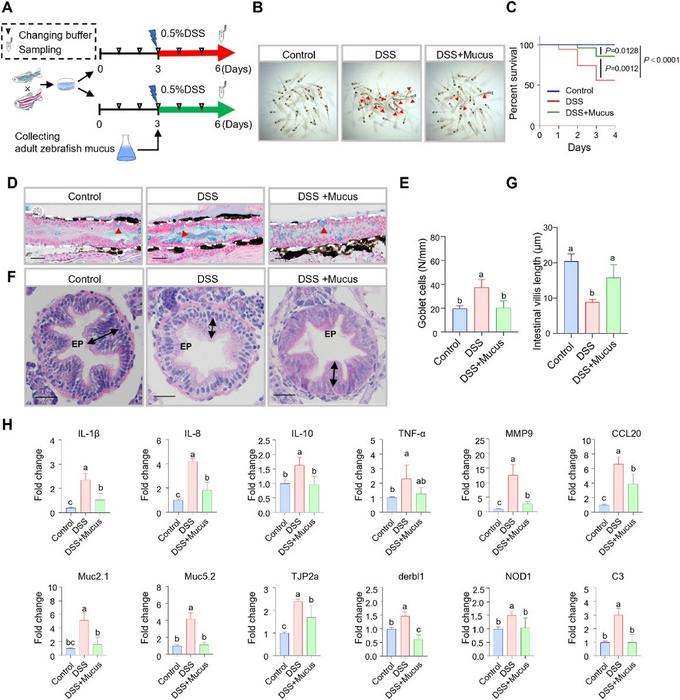
“The role of zebrafish adult mucus in dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced inflammatory response and microbial imbalance was studied through the morphology of zebrafish larvae, changes in intestinal pathology, changes in expression of immune genes, fluorescence imaging of immune cells, and changes in microbial composition and structure,” shares corresponding author Zhen Xu.
The team found that mortality rate of larvae and the number of goblet cells in intestines decreased. Meanwhile, height of the intestinal villi was enhanced, weakening the expression of immune-related genes.
“Further, the infiltration of neutrophils and macrophages in the intestine of larvae was effectively mitigated,” adds Xu. “Notably, adult zebrafish mucus can significantly upregulate the abundance of beneficial bacteria and regulate the microbiota to reach a new equilibrium.”
The results of this study, published in Water Biology and Security, indicate that adult zebrafish mucus plays an important immunomodulatory role in the immune response induced by DSS in larvae, and that adult mucus may be also used as a form of maternal immunity with an immunomodulatory function that is similar to that of mammalian milk.
“Meanwhile, adult fish mucus can be used as a potential protective and therapeutic measure to enhance the immunity of larvae in aquaculture, improve the survival rate, prevent mass mortality of fish in the early stages of life, and play a function in breeding, immunity and other aspects to promote the sustainable development of aquaculture in China,” says Xu.
###
Contact the author: Zixuan Wang, Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 18815349866@163.com ; Zhen Xu, Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, zhenxu@ihb.ac.cn
The publisher KeAi was established by Elsevier and China Science Publishing & Media Ltd to unfold quality research globally. In 2013, our focus shifted to open access publishing. We now proudly publish more than 100 world-class, open access, English language journals, spanning all scientific disciplines. Many of these are titles we publish in partnership with prestigious societies and academic institutions, such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
Journal
Water Biology and Security
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
The crucial role of fish mucus in regulating progeny inflammation and microbial homeostasis
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. Zhen Xu is an editorial board member for Water Biology and Security and was not involved in the editorial review or the decision to publish this article.