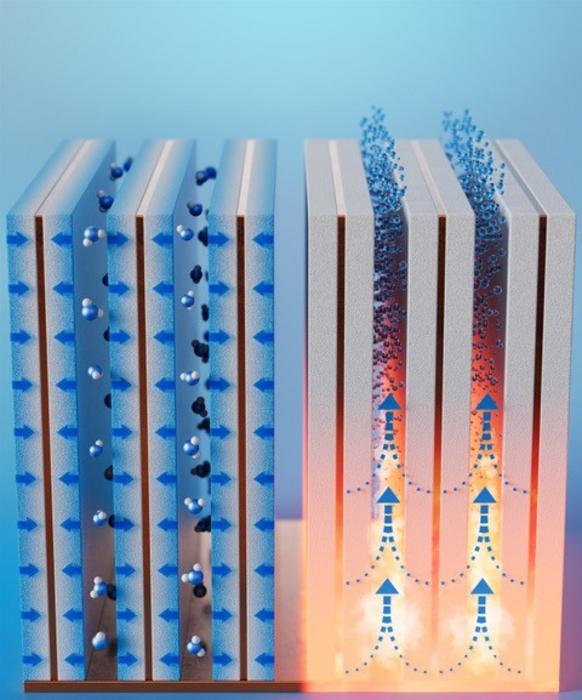
Clean, safe water is a limited resource and access to it depends on local bodies of water. But even dry regions have some water vapor in the air. To harvest small amounts of humidity, researchers in ACS Energy Letters have developed a compact device with absorbent-coated fins that first trap moisture and then generate potable water when heated. They say the prototype could help meet growing demands for water, especially in arid locations.

Credit: Xiangyu Li
Clean, safe water is a limited resource and access to it depends on local bodies of water. But even dry regions have some water vapor in the air. To harvest small amounts of humidity, researchers in ACS Energy Letters have developed a compact device with absorbent-coated fins that first trap moisture and then generate potable water when heated. They say the prototype could help meet growing demands for water, especially in arid locations.
Earth’s atmosphere holds trillions of liters of fresh water as vapor, but it’s challenging to collect this colorless, transparent and dilute gas. Previously, researchers developed systems that trap dew or fog, pooling the liquid into containers. But in dry areas that don’t have much dew, special materials like temperature-responsive hydrogels, metal-organic frameworks or zeolites (crystalline aluminosilicates) may help pull small amounts of moisture from the air and release the water when heated. However, for these absorbents to be practical for real-world use, they need to be incorporated into compact and portable devices with a waste heat source, such as applications that run at high temperatures or systems that emit heat as a by-product. So, Xiangyu Li, Bachir El Fil and colleagues developed a humidity harvester that could fit those specifications.
The researchers designed water-adsorbent “fins” by sandwiching a copper sheet between copper foams coated in a commercially available zeolite. Compared to previous studies that focused on material development, the authors say that the co-design of the adsorption bed with material properties resulted in thin adsorbent fins, which are compact and can quickly harvest water. For proof-of-concept demonstrations, they created a device with 10 small adsorbent fins placed side by side on a copper base plate about 2 millimeters apart, a distance that maximizes moisture capture from desert-like air containing 10% relative humidity. Within an hour, the fins saturated and then released the trapped moisture once the base reached 363 Fahrenheit. Extrapolating to 24 collection-release cycles, the team calculated that 1 liter of absorbent coating on the fins could produce up to 1.3 liters of potable water per day in air with 30% relative humidity — a volume two to five times greater than previously developed devices.
The work identifies a key opportunity for rapid moisture capture and water harvesting from dry air, multiple times per day. With further development, this system could be integrated into existing infrastructures that produce waste heat, such as buildings or transportation vehicles, to provide a cost-effective option for generating potable water in arid regions, the researchers say.
The authors acknowledge funding from the U.S. Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency and the Swiss National Science Foundation through a Postdoc. Mobility grant.
The paper’s abstract will be available on June 26 at 8 a.m. Eastern time here:
For more of the latest research news, register for our upcoming meeting, ACS Fall 2024. Journalists and public information officers are encouraged to apply for complimentary press registration by completing this form.
###
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note: ACS does not conduct research, but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies.
Follow us: X, formerly Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
Journal
ACS Energy Letters
Article Title
Design of a Compact Multicyclic High-Performance Atmospheric Water Harvester for Arid Environments
Article Publication Date
26-Jun-2024