This study is led by Prof. Bin Dong (Beijing International Center for Mathematical Research, Peking University) and Prof. Lin Shen (Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and Translational Research (Ministry of Education), Peking University Cancer Hospital and Institute).

Credit: ©Science China Press
This study is led by Prof. Bin Dong (Beijing International Center for Mathematical Research, Peking University) and Prof. Lin Shen (Department of Gastrointestinal Oncology, Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and Translational Research (Ministry of Education), Peking University Cancer Hospital and Institute).
With the onset of the 21st century marked by a staggering growth in artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities, we have witnessed groundbreaking advancements and transformations across various industries. Particularly in the medical field, such transformations are even more pronounced. However, while AI has unveiled countless new opportunities and possibilities for us, it also sheds light on the profound complexity inherent in medical processes. When considering key stages like diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis, the real-world medical data we grapple with is incredibly diverse and intricate. Doctors, when dealing with this data, not only refer to a vast and complicated body of standard medical knowledge but also need to craft individualized treatment plans based on the unique circumstances of each patient. Furthermore, medical examinations are multimodal, encompassing domains like pathology, radiology, and genomics. Faced with such a scenario, integrating this plethora of data and information to form a coherent and comprehensive diagnosis and treatment strategy is undeniably challenging. Most of the current tools are isolated for single tasks, implying that clinical doctors must engage in more holistic analysis and judgment during decision-making. Hence, there’s an urgent need for powerful intelligent assistance tools to aid these physicians. This is precisely what large language models (LLMs), like GPT-4, offer. Not only can they help doctors consolidate and interpret intricate data, but they also provide insights grounded in extensive knowledge,7 thus ensuring more efficient and precise assistance in pivotal stages like diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis.1, 5, 8 With the aid of such intelligent tools, we aspire to delve deeper into a patient’s genuine situation and make more apt and accurate medical decisions.
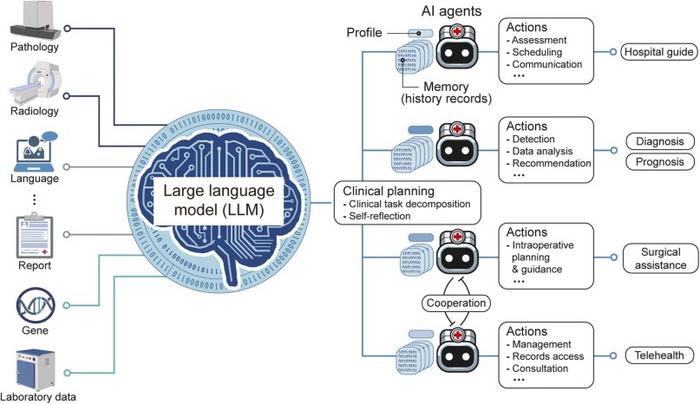
In this context, LLMs such as GPT-4, ChatGPT, and Claude have gradually made their mark in the medical domain. Taking GPT-4 as an example, its exceptional performance in the United States Medical Licensing Examinations (USMLE) has far exceeded the expectations of many experts. Yet, this is only the tip of the iceberg. While the practical application of LLMs in healthcare is still in its early stages, preliminary research has already unveiled their tremendous potential in specialized medical research and potential clinical decision support. Especially in tasks involving the integration of multimodal medical data from pathology, radiology, and genomics, LLMs have exhibited their unique ability for in-depth interpretation and linkage. Of course, their practical effects and values in real medical environments still require further study and validation. With the introduction of these advanced tools, we not only anticipate efficient consolidation of multisource medical data but also expect AI agents to offer support in predictive analysis and patient management for physicians. For instance, AI agents could assist in analyzing patient histories, laboratory results, and radiological data, subsequently providing data-driven diagnostic suggestions. Moreover, these tools can further help doctors in choosing the optimal treatment plan from a plethora of options, ensuring patients receive individualized and optimal therapeutic outcomes. Through this approach, we can look forward to a medical decision-making process that is not only more scientific but also more systematic, ensuring patients receive the best medical care.
Given the outstanding potential of LLMs in medicine, the study aims to conduct a systematic and progressive review of the recent advances achieved by LLMs in this field. It highlights the use of both general and specialized medical LLMs, primarily focusing on text-based interactions. Traditional unimodal approaches often overlook the complex multimodal nature of the medical field, prompting the development of multimodal LLMs that enhance diagnostic accuracy and efficacy. Despite notable advancements, challenges such as achieving true personalization, maintaining ongoing model updates, and equipping AI with complex problem-solving abilities remain. In this context, LLM-driven autonomous agents emerge as promising tools with diverse applications in healthcare. Moreover, assessing the efficacy and safety of medical LLMs is crucial. This review’s importance lies in shedding light on the current role of LLMs in healthcare, assessing their transformative effects on medical practices, and identifying obstacles to be addressed to fully leverage their potential in enhancing patient care and advancing medical science.
Journal
Medicine Plus