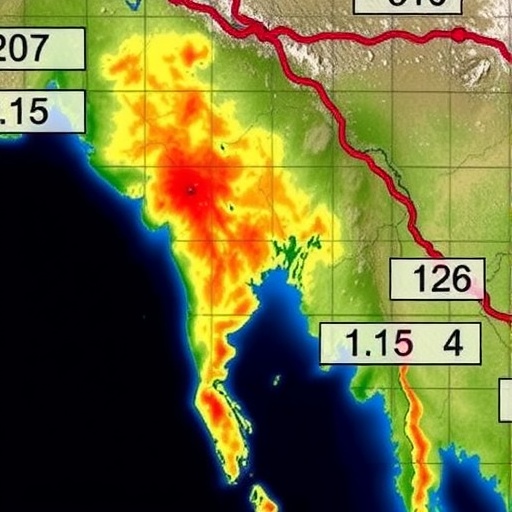
On October 2025, a pivotal study emerges from the realms of seismology, intriguing professionals and enthusiasts alike with its profound insights into the seismic activities linked to the anticipated 2025 Myanmar earthquake. This study, conducted by researchers Wang, Wen, and Peng, leverages state-of-the-art ground motion simulations to explore the integrated effects of both source and site on seismic intensity. By applying the stochastic finite-fault method, this research advances our understanding of earthquakes—an area that has historically challenged geoscientists and policymakers.
Seismic activities are shaped by various factors, and this study underscores the importance of joint examinations of the source and site effects. Traditional analyses often isolate these factors, potentially overlooking critical interactions that influence the final assessment of seismic intensities. The research elucidates how these dual influences contribute to variations in earthquake impacts across different geographic locations, providing a nuanced understanding that could lead to improved preparedness and mitigation strategies.
At the core of Wang, Wen, and Peng’s work lies the innovative stochastic finite-fault method, a computational technique that allows for the simulation of ground motions. This method models the complex slip distributions along the earthquake fault, offering a refined representation of how stress and energy release propagate through the Earth’s crust. By simulating three-component ground motions—accounting for both vertical and horizontal motions—this approach reveals a more comprehensive picture of how seismic waves travel from the source to the site.
The significance of this study is amplified given Myanmar’s seismic context, a region historically prone to significant earthquakes. This geopolitical landscape necessitates urgent attention to the nature of seismic risks, as urban development continues to stretch into vulnerable areas. By exploring the specific characteristics of the 2025 Myanmar earthquake, the authors contribute vital data that could inform urban planning and disaster readiness efforts, ultimately saving lives and minimizing destruction.
One of the standout features of this research is its application of integrated analyses. Wang and colleagues employed advanced statistical techniques to synthesize data from diverse sources, thereby enhancing the reliability of their results. This method offers an innovative perspective, revealing interdependencies among various geological and geophysical parameters. Such approaches not only streamline data interpretation but also foster collaboration amongst geoscientists, engineers, and policy-making bodies.
Discussing the implications of their findings, the authors emphasize the critical need for adaptive building codes that reflect local seismic risks informed by this research. Integrating site-specific data into engineering practices can mitigate damage and enhance the durability of structures in the event of an earthquake. This strikingly aligns with global trends advocating for more resilient urban designs—particularly pertinent as the world grapples with climate change and its implications for natural disaster occurrences.
In addition to its practical applications, the study raises philosophical questions about humanity’s relationship with natural forces, where understanding seismic phenomena becomes not just a scientific endeavor, but a moral imperative. With Inuit tales highlighting their understanding of natural events, this study echoes those stories in a modern scientific context, framing preparedness and knowledge as vital components of survival in disaster-prone areas.
To support their assertions, the authors present an extensive review of historical seismic activities in Myanmar, contextualizing their findings within past events. By correlating previous earthquake data with their current simulations, they are able to draw parallels and note discrepancies that enhance the overall credibility of their predictions. The clarity and accuracy of their models not only shed light on the expected behavior of seismic waves but also instill a notion of urgency among communities at risk.
Furthermore, the research paves the way for future scholarship in the field of geophysics. By establishing a baseline for integrated source-site analysis, upcoming studies may now expand upon these methodologies, innovating further in the realm of earthquake preparedness. With a foundation built on rigorous statistical analysis and substantive modeling, the potential for new discoveries and soothed anxieties surrounding seismic activity grows exponentially.
The profound impact of the research is also evident in its appeal to various stakeholders including academics, engineers, urban planners, and government officials. A multipronged approach ensures that the findings resonate beyond the confines of traditional scientific discussions, bridging gaps between disciplines. Collaboratives formed on these discussions are poised to elevate the standards for seismic risk management, incorporating dynamic responses informed by empirical evidence.
Despite the technical rigor of the study, Wang et al. possess an astute awareness of the social dimensions of seismic preparedness. They urge concerted efforts to engage local communities in understanding earthquake dangers and response strategies. Programs aimed at educating residents can empower individuals to act decisively during seismic events, fostering resilience and cohesion amid crises.
In summation, the research conducted by Wang, Wen, and Peng lays bare the intricate dance between seismic sources and geophysical sites, offering a roadmap for understanding and mitigating the multifaceted risks associated with earthquakes. The innovative use of the stochastic finite-fault method signals a promising frontier in seismic research—one that not only deepens scientific inquiry but also champions community-engaged scholarship as a means of safeguarding the future.
The implications of this study will undoubtedly echo through the realms of academia, engineering, and policy-making, marking a watershed moment in our collective efforts to navigate the uncertainties of seismic phenomena. The proprietary elements of their methodology will likely inspire a wave of follow-up studies, each striving to further decode the complexities of earthquakes as we seek to coexist with these powerful forces of nature.
As the world moves forward, the insights gleaned from this research are positioned to transform approaches toward seismic awareness, preparedness, and sustainability. By fostering interdisciplinary collaboration and applying cutting-edge methodologies, we inch closer to mitigating the ramifications of future earthquakes, guiding societies to weather the storms of uncertainty with informed resilience.
Subject of Research: Integrated source-site effects on seismic intensity in earthquake prediction and analysis.
Article Title: Integrated source-site effects on seismic intensity in the 2025 Myanmar earthquake from the three-component ground motion simulations by stochastic finite-fault method.
Article References:
Wang, H., Wen, R., Peng, Z. et al. Integrated source-site effects on seismic intensity in the 2025 Myanmar earthquake from the three-component ground motion simulations by stochastic finite-fault method.
Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 24, 901–915 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11803-025-2344-2
Image Credits: AI Generated
DOI:
Keywords: Seismic intensity, source-site effects, ground motion simulations, stochastic finite-fault method, earthquake risk management, Myanmar earthquake, engineering practices, urban planning, community resilience.